AWS Organizations
- Global Service used to manage multiple AWS accounts centrally.
- The main account is called the Master Account, and other linked accounts are Child Accounts.
Key Benefits
- Consolidated Billing
- All accounts share a single payment method managed by the master account.
- You receive one combined bill for all linked accounts.
- Pricing Benefits
- Aggregated usage provides volume discounts for services like EC2 and S3 across all accounts.
- Reserved Instances (RIs) are shared among accounts for maximum savings.
- Automation
- API support to automate AWS account creation (useful for sandbox or departmental accounts).
- Service Control Policies (SCPs)
- Used to restrict account privileges.
- Common exam topic.
Multi-Account Strategy
Why Use Multiple Accounts
- Easier management and security isolation.
- Organize by:
- Department (Sales, Finance, HR)
- Environment (Dev, Test, Prod)
- Project (Project-1, Project-2, etc.)
- Regulatory requirements (compliance-based isolation)
Benefits
- Separate service limits per account.
- Improved resource isolation (different VPCs per account).
- Dedicated logging accounts for central log management.
Best Practices
- Apply tagging standards across accounts for billing.
- Enable CloudTrail and CloudWatch Logs in all accounts.
- Send logs to a central S3 or logging account for visibility and compliance.
Organizational Units (OUs)
- Used to group related accounts within an organization.
- Structure Example:
- Root OU (contains Master Account)
- Dev OU, Prod OU, etc.
- Nested OUs possible (e.g., Prod → Finance OU, HR OU).
- Allows hierarchical policy management using SCPs.
Service Control Policies (SCPs)
- Manage permissions centrally across accounts.
- Whitelist or blacklist IAM actions at OU or account level.
- Do not apply to the Master Account.
Behavior
- Affect users and roles (including root users) within child accounts.
- Do not affect service-linked roles (used internally by AWS services).
- SCPs must have explicit “Allow” statements; otherwise, actions are denied by default.
Use Cases
- Restrict access to specific AWS services (e.g., deny EMR in production).
- Enforce compliance (e.g., disable non-PCI-compliant services).
Examples
- Blacklist example:
| |
- Denies all DynamoDB actions.
- Whitelist example:
| |
- Allows only EC2 and CloudWatch actions; all others denied.
Key Exam Points
- AWS Organizations = Global Service for multi-account management.
- Master account pays bills via Consolidated Billing.
- Aggregated usage and shared RIs reduce costs.
- SCPs manage account-level permissions, not IAM roles directly.
- SCPs don’t apply to the master account or service-linked roles.
- Use CloudTrail and centralized logging for auditing all accounts.
AWS Organizations – Consolidated Billing
Purpose
Consolidated Billing in AWS Organizations allows centralized payment management and shared cost benefits across multiple AWS accounts under one organization.
Key Features
- One Bill for All Accounts
- The management (master) account pays the bill for all linked accounts.
- Simplifies financial management for the accounting department.
- No limit on how many accounts can be created and managed.
- Combined (Aggregated) Usage
- All usage across accounts is aggregated to benefit from volume discounts.
- Example:
- S3 offers lower pricing after 5 TB.
- If six accounts each use 1 TB, combined usage (6 TB) qualifies for discounted pricing.
- Shared Reserved Instances (RI) and Savings Plans
- RI or Savings Plan discounts purchased in one account automatically apply across all accounts in the organization.
- Maximizes cost efficiency.
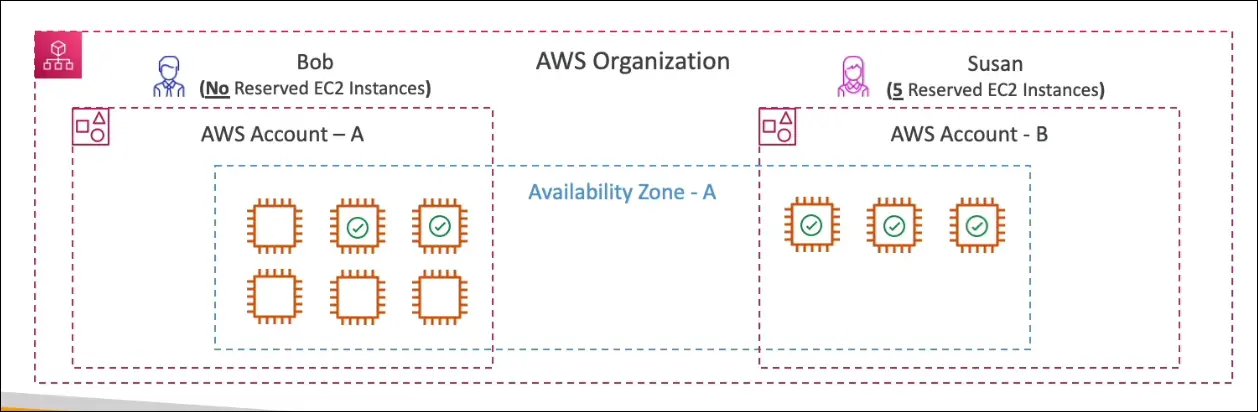
Example: Reserved Instance Sharing
- Scenario:
- Organization has two accounts: A and B.
- Account B has 5 reserved EC2 instances.
- Across both accounts, 9 EC2 instances are running in the same Availability Zone (AZ).
- Outcome:
- 3 instances in Account B use 3 of the 5 RIs.
- 2 of the remaining RIs apply to instances in Account A.
- Result: 5 instances receive RI pricing, 4 instances are on-demand.
- This demonstrates cross-account RI sharing.
Important Notes
- Shared Volume Pricing: Combined usage discounts apply across all linked accounts.
- Shared RI/Savings Plan: Enables efficient cost savings across accounts.
- Optional Control: RI/Savings Plan discount sharing can be disabled for specific accounts, including the management account.
- Exam Tip: Know the benefits of combined usage, RI sharing, and the effect of turning sharing off.
Summary
Consolidated Billing under AWS Organizations provides:
- Centralized billing management.
- Aggregated usage discounts.
- Shared Reserved Instance and Savings Plan pricing.
- Flexibility to manage billing preferences per account.
AWS Control Tower
Purpose
AWS Control Tower provides an easy, automated way to set up and govern a secure, compliant, multi-account AWS environment based on AWS best practices.
Why It Exists
Without Control Tower, users must manually:
- Create an AWS Organization
- Configure accounts
- Apply security and compliance settings manually
Control Tower automates all these steps with just a few clicks.
Key Features & Benefits
- Automated Setup
- Quickly creates a multi-account AWS environment.
- Automatically sets up AWS Organizations, organizational units (OUs), and accounts.
- Automated Policy Management (Guardrails)
- Guardrails = Preconfigured rules that enforce or monitor compliance.
- Can be preventive (block non-compliant actions) or detective (alert on violations).
- Continuous Compliance
- Detects and remediates policy violations automatically.
- Compliance Dashboard
- Provides a visual, interactive dashboard to track compliance status across all accounts.
- Integration with AWS Organizations
- Runs on top of AWS Organizations.
- Automatically applies Service Control Policies (SCPs) to enforce guardrails effectively.
Service Control Policies (SCPs)
- Used by Control Tower to restrict or allow certain AWS actions across accounts.
- Help ensure all accounts comply with organization-wide governance rules.
Summary
AWS Control Tower helps:
- Simplify multi-account setup and governance.
- Automate security and compliance management.
- Maintain organization-wide visibility and control.
Exam Tip:
Control Tower = Automated governance and best-practice setup for multi-account AWS environments using guardrails and SCPs on top of AWS Organizations.
AWS Control Tower
Purpose
AWS Control Tower provides an easy, automated way to set up and govern a secure, compliant, multi-account AWS environment based on AWS best practices.
Why It Exists
Without Control Tower, users must manually:
- Create an AWS Organization
- Configure accounts
- Apply security and compliance settings manually
Control Tower automates all these steps with just a few clicks.
Key Features & Benefits
- Automated Setup
- Quickly creates a multi-account AWS environment.
- Automatically sets up AWS Organizations, organizational units (OUs), and accounts.
- Automated Policy Management (Guardrails)
- Guardrails = Preconfigured rules that enforce or monitor compliance.
- Can be preventive (block non-compliant actions) or detective (alert on violations).
- Continuous Compliance
- Detects and remediates policy violations automatically.
- Compliance Dashboard
- Provides a visual, interactive dashboard to track compliance status across all accounts.
- Integration with AWS Organizations
- Runs on top of AWS Organizations.
- Automatically applies Service Control Policies (SCPs) to enforce guardrails effectively.
Service Control Policies (SCPs)
- Used by Control Tower to restrict or allow certain AWS actions across accounts.
- Help ensure all accounts comply with organization-wide governance rules.
Summary
AWS Control Tower helps:
- Simplify multi-account setup and governance.
- Automate security and compliance management.
- Maintain organization-wide visibility and control.
Exam Tip:
Control Tower = Automated governance and best-practice setup for multi-account AWS environments using guardrails and SCPs on top of AWS Organizations.
AWS Service Catalog
Purpose
AWS Service Catalog enables organizations to create and manage approved collections of AWS resources so that users can quickly deploy authorized products in a controlled, consistent, and compliant manner.
Problem It Solves
- New AWS users have too many choices and may create resources inconsistently with company standards.
- Service Catalog provides a self-service portal for users to launch only pre-approved resources designed by administrators.
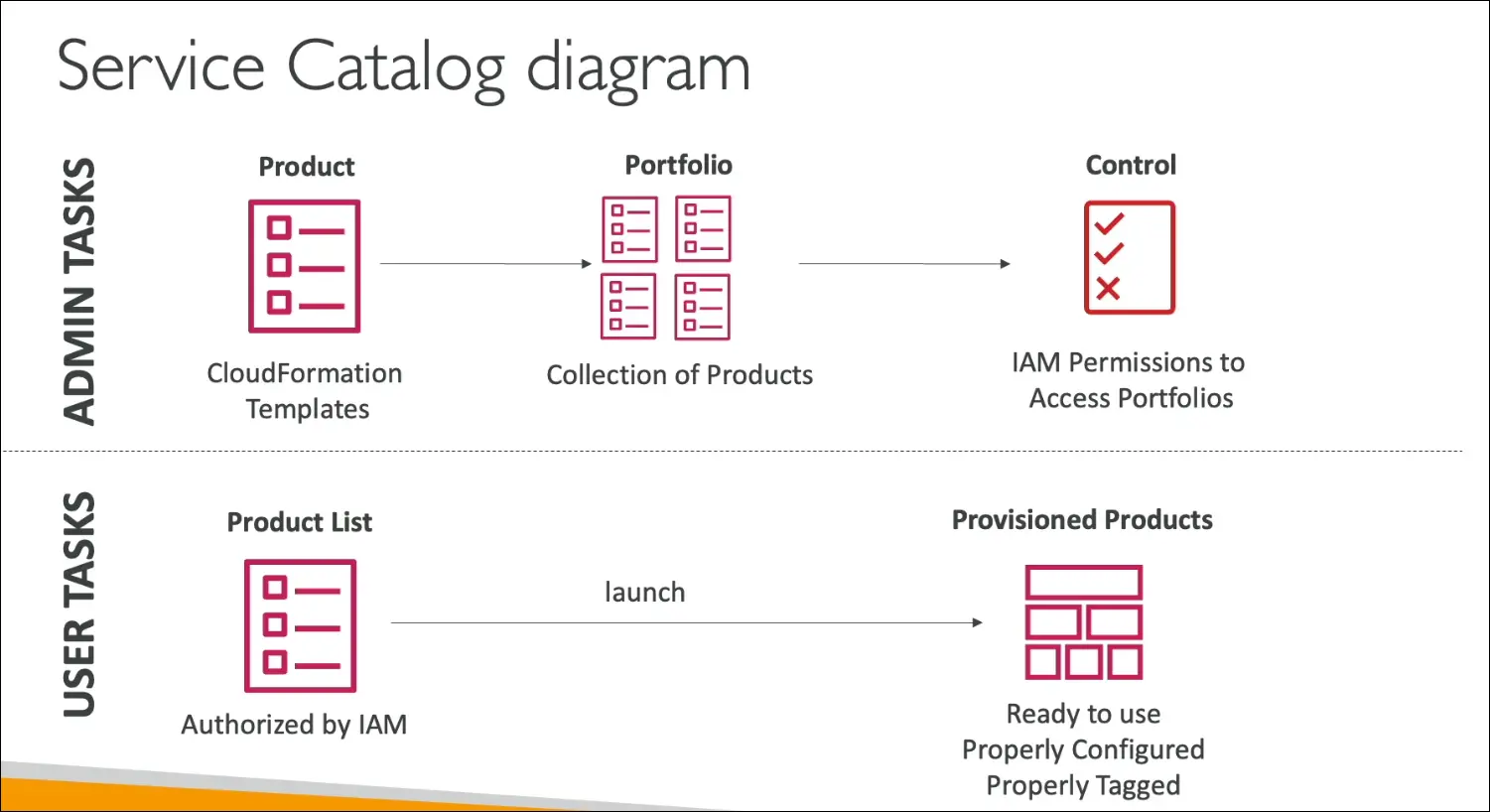
Key Concepts
- Product
- A CloudFormation template that defines a resource or set of resources (e.g., EC2, RDS, S3).
- Configured with predefined parameters (for consistency and compliance).
- Portfolio
- A collection of products created by administrators.
- Admins define who can access and launch products within each portfolio.
- Self-Service Portal
- End users can view and launch only the products they are permitted to use.
- When a product is launched, AWS CloudFormation automatically provisions it according to the approved configuration.
Benefits
- Standardization: Ensures all resources follow organizational policies and tagging standards.
- Compliance: Prevents users from launching unapproved configurations.
- Automation: Uses CloudFormation for automated, consistent provisioning.
- Access Control: Admins control which users or groups can deploy specific resources.
- Ease of Use: Provides a simple portal for non-technical users to deploy preconfigured infrastructure.
Example Scenario
- A developer wants an RDS database but doesn’t know how to configure it correctly.
- The admin creates an RDS product template in Service Catalog.
- The developer launches the database from the self-service portal with one click.
- The database is deployed correctly configured and tagged as per organization standards.
Summary
| Role | Action |
|---|---|
| Admin | Creates CloudFormation-based products, groups them in portfolios, defines permissions |
| User | Launches authorized products from the Service Catalog portal |
Exam Tip:
AWS Service Catalog = Pre-approved, self-service provisioning of AWS resources using CloudFormation templates, ensuring governance, standardization, and compliance.
AWS Pricing Models
AWS Pricing Models
AWS offers four main pricing approaches:
- Pay-As-You-Go
- Pay only for what you use.
- No long-term contracts or upfront costs.
- Start, stop, or delete resources anytime.
- Supports scalability and agility.
- Save When You Reserve
- Reserve capacity for 1 or 3 years for discounts.
- Predictable costs and compliance with long-term needs.
- Applies to EC2, RDS, DynamoDB, ElastiCache, and Redshift.
- Pay Less by Using More
- Volume-based discounts (e.g., Amazon S3).
- More usage = lower per-unit cost.
- AWS Cost Reduction
- AWS often passes infrastructure cost savings to customers as it scales.
- Result: regular price reductions over time.
Free and Always-Free AWS Services
- Completely Free: IAM, VPC, Consolidated Billing.
- Free but Resources Billed: Elastic Beanstalk, CloudFormation, Auto Scaling.
- Example: Beanstalk is free, but EC2 and ELB resources it creates are billed.
AWS Free Tier Types
- 12-Month Free Tier – For new accounts (e.g., t2.micro for one year).
- Always Free – Continues beyond 12 months (e.g., AWS Lambda, DynamoDB 25 GB).
- Trials – Short-term, typically 30-day trials (e.g., GuardDuty, SageMaker).
EC2 Pricing Models
| Model | Description | Discount |
|---|---|---|
| On-Demand | Pay per second/minute for compute usage. | None |
| Reserved Instances (RI) | 1–3-year commitment for predictable workloads. | Up to 75% |
| Spot Instances | Bid on unused capacity, can be interrupted. | Up to 90% |
| Dedicated Hosts | Physical servers dedicated to one customer. | Custom pricing |
| Savings Plans | Flexible discount plan across EC2, Fargate, Lambda. | Based on commitment |
Billing Factors: Instance type, size, OS, region, and additional features (like load balancer or CloudWatch detailed monitoring).
AWS Compute Pricing
Lambda
- Charged per API call and execution duration × memory used.
- Pay only for compute time consumed.
ECS (Elastic Container Service)
- EC2 Launch Type: No ECS fee, pay for EC2 instances.
- Fargate Launch Type: Pay per container for CPU and memory requested.
AWS Storage Pricing
Amazon S3
- Charged for: Storage used, number of requests, data transfer out, lifecycle transitions.
- Free: Data transfer into S3.
- Tiered pricing – higher usage = lower per-GB cost.
- Storage Classes: Standard, Infrequent Access (IA), One-Zone IA, Intelligent-Tiering, Glacier, Deep Archive.
Amazon EFS (Elastic File System)
- Pay per GB stored.
- Infrequent Access tier available with lifecycle rules.
Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store)
- Billed for:
- Volume size (provisioned GB, regardless of usage)
- Volume type (SSD, Magnetic, etc.)
- Provisioned IOPS (if applicable)
- Snapshots (per GB per month)
- Data transfer out (tiered)
- Free: Data written into EBS.
Database Pricing (Amazon RDS)
- Billed per hour based on:
- Database engine (MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.)
- Instance type and size
- Deployment type (Single-AZ vs Multi-AZ)
- Storage provisioned (EBS-based)
Options:
- On-Demand: No long-term commitment.
- Reserved: 1–3-year term, cheaper for predictable workloads.
- Backups: Free up to 100% of total database size.
- Data Transfer: Inbound free, outbound paid and tiered.
Key Takeaways for CCP Exam
- Know the four pricing models and when to use each.
- Understand EC2 billing models and discount tiers.
- Remember data transfer in = free, data transfer out = paid (almost always).
- Recognize which services are always free (IAM, VPC, consolidated billing).
- Be familiar with storage pricing differences (S3 vs EBS vs EFS).
- Backups and snapshots usually incur per-GB charges.
- Free tier types: 12-month, Always Free, and Trials.
AWS Savings Plans
What are Savings Plans?
A flexible pricing model that helps you save money on AWS compute services.
You commit to spend a fixed dollar amount per hour ($/hr) for 1 or 3 years, and in return, AWS gives you discounts up to 72% compared to On-Demand pricing.
You commit to a spending amount, not specific instances or resources.
Simpler than Reserved Instances (no need to specify instance type, region, etc.).
Types of Savings Plans
EC2 Instance Savings Plan
- Up to 72% discount over On-Demand.
- Commitment applies to specific instance family in a specific region.
Example: Commit $10/hour for C5 family in a region. - Flexible across:
- Availability Zones
- Instance sizes (e.g.,
c5.xlarge,c5.4xlarge) - OS (Linux, Windows)
- Tenancy (shared or dedicated)
- Payment options:
- All Upfront → biggest discount
- Partial Upfront
- No Upfront
Compute Savings Plan
- Up to 66% discount.
- Most flexible option.
- Applies across regions, instance families, sizes, OS, and tenancy.
- Covers multiple compute services:
- EC2
- AWS Fargate (containers)
- AWS Lambda (serverless)
- You simply commit to a dollar/hour spend, and AWS applies discounts automatically.
Machine Learning Savings Plan (SageMaker)
- Applies to Amazon SageMaker workloads.
- Example: Using an
ml.t3.largenotebook long-term can save ~28%. - Discounts depend on usage type and duration.
How to Set Up a Savings Plan
- Go to AWS Cost Explorer.
- AWS recommends the right Savings Plan based on your usage.
- You can also estimate pricing via the Savings Plan calculator.
Options to configure:
- Plan Type (EC2, Compute, or SageMaker)
- Term (1 or 3 years)
- Payment (All, Partial, or No Upfront)
- Commitment ($/hour)
Example Scenario
You commit to $500/hour spend for 3 years, partial upfront.
AWS shows:
- Upfront cost
- Monthly payment
- Total estimated savings
Then you simply add it to cart, and your plan applies automatically to matching resources.
Key Takeaways
- Savings Plans > Reserved Instances (simpler and more flexible).
- Compute Savings Plan = most flexible, covers EC2, Lambda, Fargate.
- EC2 Instance Plan = most savings, but less flexible.
- Machine Learning Plan = specialized for SageMaker.
- Commit to a spend amount, not instance specs.
- Managed via Cost Explorer or Billing Console.
AWS Compute Optimizer
Purpose:
- Helps reduce costs and improve performance by recommending optimal AWS resources for workloads.
- Uses machine learning to analyze current configurations and CloudWatch metrics.
How it Works
- Analyzes:
- EC2 instances
- Auto Scaling Groups
- EBS volumes
- Lambda functions
- Identifies over-provisioned and under-provisioned resources.
- Provides recommendations for right-sizing.
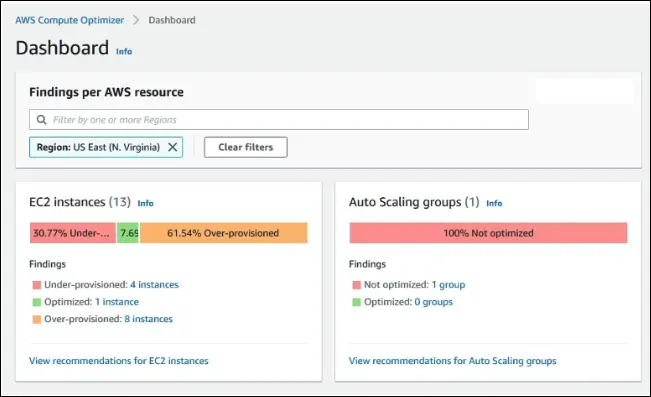
Benefits
- Improves cost-efficiency and performance.
- Can reduce costs by up to 25%.
- Recommendations can be exported to Amazon S3.
Key Features
- Uses historical utilization metrics via CloudWatch.
- Offers automated, ML-based suggestions.
- Helps maintain the right balance between performance and cost.
AWS Billing and Costing Tools
Purpose
These tools help you estimate, track, and monitor your AWS costs effectively.
You must know all of them for the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CCP) exam.
Estimate Costs
AWS Pricing Calculator
- Used before deployment to estimate the cost of AWS services.
- Lets you model your architecture and forecast monthly charges.
- You can share and save your estimates.
Track Costs
Billing Dashboard
- Found in the AWS Management Console.
- Gives an overview of current and historical spending.
- Allows quick access to bills, payment history, and cost breakdown.
Cost Allocation Tags
- Helps organize and track costs by assigning metadata (tags) to resources.
- Example: Tag resources by project, department, or environment.
- Costs are then grouped in reports for better tracking.
Cost and Usage Report (CUR)
- Most detailed report on AWS costs and usage.
- Includes resource-level data, updated daily.
- Often exported to Amazon S3 for analysis.
- Can be integrated with tools like Athena, Redshift, or QuickSight.
Cost Explorer
- Interactive tool to analyze and visualize spending patterns over time.
- Can filter and group costs by service, tag, or linked account.
- Helps identify trends, anomalies, and savings opportunities.
Monitor & Control Costs
Billing Alarms
- Set up through Amazon CloudWatch.
- Sends alerts (via SNS) when spending exceeds a threshold.
- Useful for staying within your budget.
AWS Budgets
- Allows you to set custom cost and usage budgets.
- Alerts you when actual or forecasted usage exceeds thresholds.
- Can track:
- Cost budgets
- Usage budgets
- Reservation or Savings Plan utilization
Exam Tip
| Category | Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Estimate | AWS Pricing Calculator | Forecast cost before using services |
| Track | Billing Dashboard, Cost Allocation Tags, CUR, Cost Explorer | Track and analyze ongoing spending |
| Monitor | Billing Alarms, AWS Budgets | Set alerts and maintain control over spending |
AWS Pricing Calculator (Cost Estimation Tool)
Overview
- Purpose: Used to estimate costs for AWS solutions before deployment.
- URL: https://calculator.aws/
- Use Case: Helps architects and developers forecast how much a designed architecture will cost per month or year.
Main Features
Create Estimates:
- Select AWS services (for example, EC2, S3, RDS, etc.).
- Configure them based on expected usage and resources.
- Get detailed cost estimates per service and per month/year.
Example Walkthrough (EC2):
- Select Amazon EC2.
- Choose Region (for example,
US-East-1). - Define workload type: Quick or Advanced estimate.
- OS: Linux.
- Instance type: T4g.xlarge (4 vCPUs, 16 GB RAM).
- Quantity: 4 instances.
- Utilization: 80% per month.
- Pricing strategy: EC2 Instance Savings Plan, 1-year, no upfront payment.
- Add EBS storage: 200 GB per instance.
- Add the configuration to the estimate.
Add Additional Services (Example):
- Add Elastic Load Balancer (ALB):
- Region: same as EC2.
- Quantity: 1 ALB.
- Data processed: ~5 GB/hour.
- ~5 new connections per second.
- Add to estimate again.
- Add Elastic Load Balancer (ALB):
Final Estimate Example:
- Total 12-month cost: ≈ $4,500 USD for this small architecture.
- Calculator shows cost per service and per month.
Key Capabilities
- Supports dozens of AWS services.
- Allows granular configurations (compute, storage, bandwidth, requests, etc.).
- Lets you:
- Create resource groups.
- Add AWS Support plans.
- Share or export estimates.
- Save multiple scenarios for comparison.
Key Takeaways
- The AWS Pricing Calculator is used before deployment to forecast AWS costs.
- It’s not tied to your account (you don’t need AWS credentials to use it).
- Commonly used for:
- Project planning.
- Budget approvals.
- Cost comparison between architectures or regions.
AWS Cost Tracking and Management
Billing Dashboard
- The Billing Dashboard shows:
- Current month’s cost, forecast, and month-to-date usage.
- A cost breakdown by service and by month.
- Links to the Free Tier Dashboard, showing how much of your free tier usage has been consumed.
- You can access it from the AWS console:
- Click on your account name (top right) → Billing and Cost Management
- Or search for Billing in the AWS search bar.
Free Tier Dashboard
Displays:
- Service name, current usage, and forecasted usage.
- Free tier limits per service.
Helps you monitor if you’re close to exceeding free tier limits.
Example: Lambda or SQS may reach the free limit, but SNS might still have free requests left.
Cost Allocation Tags
Purpose
- Tags help you organize resources and track costs more effectively.
- Used to group costs by department, team, application, environment, etc.
Types of Tags
AWS-Generated Tags
- Automatically applied.
- Start with the prefix
aws:(e.g.,aws:createdBy).
User-Defined Tags
- Created manually.
- Start with
user:(e.g.,user:team,user:cost-center).
Common Tag Examples
NameEnvironment(dev, test, prod)TeamCostCenterDepartment
Tag Editor & Resource Groups
- Access via Resource Groups in the console → Tag Editor.
- You can:
- Search resources (like EC2, RDS, Security Groups).
- Add/edit tags (e.g.,
Department: IT).
- Then, create Resource Groups based on tags to easily manage related resources.
- Example: Group all resources tagged
Department=IT.
- Example: Group all resources tagged
Cost Allocation Reports
- After tagging resources:
- Go to Billing → Cost Allocation Tags.
- Activate the tags you want to include in cost reports.
- AWS will then generate cost reports grouped by those tags.
- Reports can be exported (e.g., to Excel) for deeper analysis.
In Short
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Billing Dashboard | Overview of costs, forecast, and usage. |
| Free Tier Dashboard | Tracks your free-tier consumption. |
| Tags | Organize and group resources logically. |
| Tag Editor | Add or modify tags in bulk. |
| Resource Groups | Manage collections of tagged resources. |
| Cost Allocation Reports | Track costs by tags (department, app, team, etc.). |
AWS Billing Monitoring and Budgets
Billing Metric
- The billing metric is available in Amazon CloudWatch, but only in the region
us-east-1(N. Virginia). - It aggregates all AWS costs across all regions into a single metric.
- The metric tracks actual cost, not forecasted cost.
- This data can be visualized as a graph showing cost over time.
Billing Alarms
- You can create a Billing Alarm using the billing metric in CloudWatch.
- Example: You can set an alarm to trigger when total cost exceeds $70.
- When the alarm is triggered, AWS can send an email notification through Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service).
- Billing alarms are simple and basic, mainly for alerting when a threshold is crossed.
- However, they are less powerful than AWS Budgets, which provide deeper insights and more customization.
AWS Budgets
AWS Budgets allow detailed monitoring of costs, usage, and reservations, with alerts and forecasts.
Purpose
- Sends alerts when:
- Actual cost/usage exceeds the defined budget.
- Forecasted cost/usage is expected to exceed the budget.
Types of Budgets
- Cost Budget — Track how much money you spend.
- Usage Budget — Track usage of specific resources (e.g., EC2 hours, S3 GB).
- Reservation Budget — Monitor Reserved Instance utilization.
- Savings Plan Budget — Monitor Savings Plan utilization.
Supported Services for RI Budgets
- EC2, RDS, Redshift, and ElastiCache Reserved Instances.
Notifications
- Supports up to 5 SNS notifications per budget.
- You can send emails, trigger Lambda functions, or integrate with automation.
- You can filter budgets by:
- Service (e.g., EC2, S3)
- Linked account (in Organizations)
- Tag
- Purchase option
- Instance type
- Region or Availability Zone
- API Operation, etc.
Cost
- First two budgets are free.
- After that, $0.02 per day per budget.
Creating a Budget (Demo Walkthrough)
Step 1: Go to AWS Budgets Console
- Search “Budgets” in the AWS Console.
- You’ll see existing budgets (e.g., “Don’t go over $10”) and their usage vs forecast.
Step 2: Create a New Budget
- Choose:
- Use Template (predefined)
- Or Customize your own (Cost, Usage, Savings Plan, or Reservation)
Step 3: Set Details
- Budget name: e.g.,
DemoBudget - Period: Monthly, Quarterly, Annually, or Daily
- Type: Recurring or Expiring
- Start and End Date
- Budget amount: e.g., $10
Step 4: Filter Scope
- Apply filters like:
- Service =
EC2-Other - Or only monitor costs from
Key Management Service (KMS)
- Service =
- You can combine multiple filters for fine-grained tracking.
Step 5: Set Alerts
- Example:
- Send email at 80% of actual cost (e.g., when $8 out of $10 spent)
- Send email at 80% of forecasted cost
- Add email recipients, e.g.,
stephane@example.com - Graphs will visually show budget amount, usage, and alert thresholds.
Step 6: Link to Cost Explorer
- AWS Budgets integrates with Cost Explorer, so you can drill down into your spending patterns.
In Short
| Feature | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Billing Metric | Tracks total actual AWS cost (us-east-1 only) | Basis for alarms |
| Billing Alarm | Sends alert when total cost exceeds threshold | Basic alert only |
| AWS Budgets | Advanced tracking with forecasts, filters, and multiple alerts | 4 types (Cost, Usage, RI, Savings Plan) |
| Notifications | Up to 5 per budget | Via SNS (email, Lambda, etc.) |
| Cost | First 2 free, then $0.02/day | — |
| Integration | Linked with Cost Explorer | Enables deeper analysis |
AWS Cost Anomaly Detection
Purpose:
AWS Cost Anomaly Detection helps you monitor and identify unusual spending patterns in your AWS account using machine learning.
Key Features
Machine Learning-Based Monitoring:
Uses ML to continuously analyze your cost and usage data and detect unusual spending (cost spikes or continuous increases).No Manual Thresholds Needed:
You don’t need to define any cost limits; the service automatically learns your historical spending behavior.Monitors Multiple Dimensions:
- AWS services
- Member accounts
- Cost allocation tags
- Cost categories
Automated Reports:
- Provides Anomaly Detection Reports with root cause analysis of unexpected cost changes.
Notifications:
- You can receive alerts via Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service).
- Choose between:
- Individual alerts (for each anomaly)
- Daily or weekly summaries
Benefits
- Detects cost spikes early.
- Automatically adapts to your account’s spending trends.
- Helps in root cause analysis to identify which service or resource caused the increase.
- Reduces the risk of unexpected AWS bills.

Summary
AWS Cost Anomaly Detection uses machine learning to:
- Monitor AWS costs and usage.
- Detect anomalies automatically.
- Send notifications through SNS.
- Provide detailed insights into the cause of abnormal spending.
AWS Service Quotas
Definition:
- AWS Service Quotas help you manage and monitor limits (also called quotas) for AWS resources and services.
- Every AWS account has default quotas that restrict how much of a resource you can use.
Purpose
- Prevents accidental resource overuse or cost overruns.
- Lets you track, get alerts, and request increases in limits.
Examples of Quotas
- Number of Lambda concurrent executions
- Number of EC2 instances per region
- Number of EBS volumes, etc.
Key Features
- Monitor quotas across all AWS services.
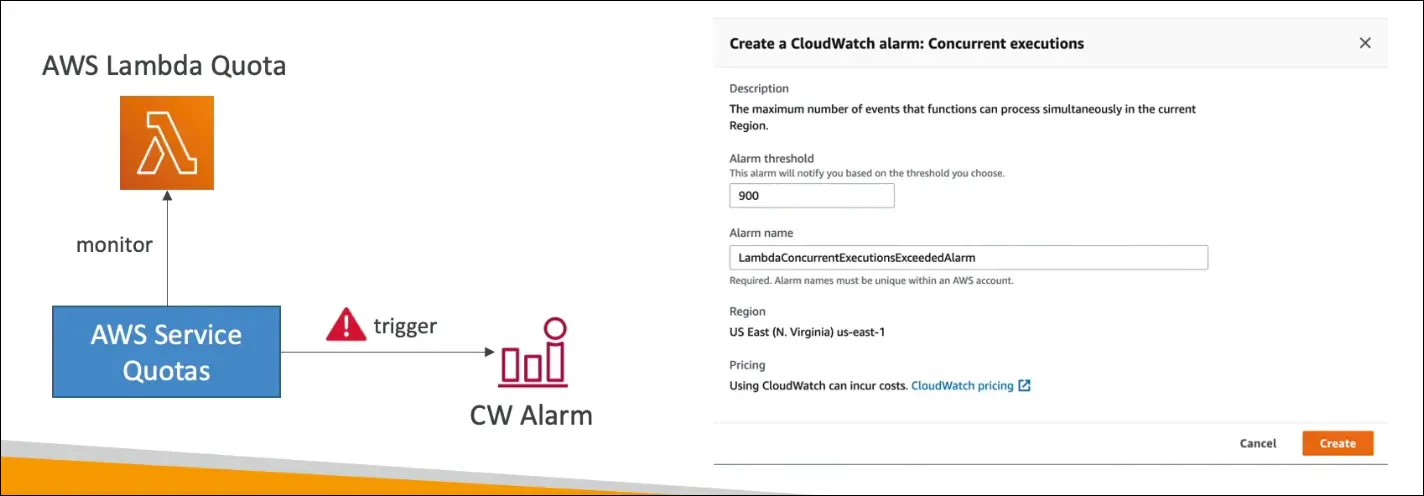
- Create CloudWatch Alarms directly from the Service Quotas console:
- Example: Get notified when Lambda concurrent executions reach 80% of the quota.
- Request quota increases directly from the console.
- Optionally shut down resources if limits are being reached unintentionally.
Summary
- Service Quotas = Centralized place to view and manage AWS limits.
- You can:
- View all quotas
- Get alerts (via CloudWatch)
- Request increases easily
AWS Trusted Advisor
Definition:
- A web-based tool that provides real-time recommendations to help you follow AWS best practices.
- No installation required, it automatically analyzes your AWS environment.
Purpose:
- Helps you optimize performance, security, and cost.
- Acts as an account assessment tool, scanning for potential issues or inefficiencies.
Trusted Advisor Checks (6 Categories):
- Cost Optimization – Detect underused or idle resources.
- Performance – Improve resource speed and efficiency.
- Security – Identify risky configurations (e.g., public S3 buckets, unrestricted security groups).
- Fault Tolerance – Increase application availability and resilience.
- Service Limits – Warn when usage approaches AWS quota limits.
- Operational Excellence – Recommend best practices for managing workloads.
Examples of Checks
- EBS or RDS public snapshots
- Use of root account
- S3 buckets with public access
- Unrestricted security group ports
- Lambda or EC2 limits approaching quota
Support Plans and Access
- Core checks – Available to all AWS users (basic checks).
- Full checks – Available only with Business or Enterprise Support Plans.
- With these plans, you also get programmatic access to Trusted Advisor through the AWS Support API.
Integration and Use
- View recommendations directly in the AWS Management Console.
- Can view Service Limits (like Auto Scaling groups, DynamoDB capacity, etc.).
- Limited use without a support plan, but valuable for security and service limit checks.
Summary
- AWS Trusted Advisor helps improve:
- Security
- Cost efficiency
- Performance
- Reliability
- Core checks are free, advanced checks require Business/Enterprise support.
AWS Accounts Best Practices
1. Multiple Accounts Management
- Use AWS Organizations to manage multiple accounts.
- Apply Service Control Policies (SCPs) to control permissions across accounts.
- Use AWS Control Tower to easily set up and manage multi-account environments following best security practices.
2. Cost and Resource Management
- Use Tags and Cost Allocation Tags for organized resource tracking and billing.
3. Security Best Practices
- Follow IAM Guidelines:
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
- Apply Least Privilege Principle.
- Enforce Password Policies and Password Rotation.
- Use a Dedicated Logging Account to store logs securely in S3 or CloudWatch Logs.
- Use CloudTrail to record all API calls for auditing.
4. Monitoring and Compliance
- Use AWS Config to track resource configurations and compliance over time.
- Use Trusted Advisor for account insights and optimization recommendations.
5. Automation and Deployment
- Use AWS CloudFormation to deploy stacks across multiple accounts and regions.
- Use AWS Service Catalog to let users launch pre-approved stacks defined by administrators.
6. Compromised Account Recovery
If an account is compromised:
- Change the root password.
- Delete all old passwords and access keys.
- Contact AWS Support immediately.
AWS Billing and Cost Management Tools
1. Compute Optimizer
- Provides recommendations to optimize resource configurations (like EC2, Lambda, etc.)
- Helps reduce costs by right-sizing resources.
2. AWS Pricing Calculator
- Used to estimate costs of AWS services before usage.
- Great for budget planning and cost forecasting.
3. Billing Dashboard
- Gives a high-level overview of your AWS spending.
- Includes a Free Tier Dashboard to monitor your free-tier usage.
4. Cost Allocation Tags
- Tag resources to categorize and track spending.
- Enables detailed cost reports filtered by your custom tags.
5. Cost and Usage Reports (CUR)
- The most detailed and comprehensive billing dataset.
- Used for deep analysis of AWS costs and usage patterns.
6. Cost Explorer
- Lets you visualize, analyze, and forecast costs and usage.
- Supports viewing data months in advance.
7. Billing Alarms
- Created in us-east-1 region.
- Track total or per-service billing using CloudWatch Alarms.
8. AWS Budgets
- Enables custom budget creation for cost and usage tracking.
- Can monitor:
- Cost and usage
- Reserved Instances (RI)
- Savings Plans
- Sends real-time alerts when you exceed thresholds.
9. Savings Plans
- Offer discounts on AWS compute usage in exchange for a 1- or 3-year commitment to a specific dollar amount per hour.
- More flexible than Reserved Instances.
10. Cost Anomaly Detection
- Uses machine learning to identify unusual spending patterns.
- Helps detect unexpected cost increases early.
11. Service Quotas
- Monitors service limits (e.g., number of EC2 instances or Lambda functions).
- Can set CloudWatch alerts when nearing limits.
- Allows requesting quota increases directly from the console.
Summary
AWS provides multiple cost management tools to help you:
- Estimate (Pricing Calculator)
- Monitor (Billing Dashboard, Cost Explorer, Budgets)
- Optimize (Compute Optimizer, Savings Plans)
- Control (Service Quotas, Cost Anomaly Detection)