AWS Cloud Integrations
Purpose of Cloud Integration
- Multiple applications often need to communicate with each other.
- AWS provides different integration patterns to enable communication between distributed systems.
Communication Patterns
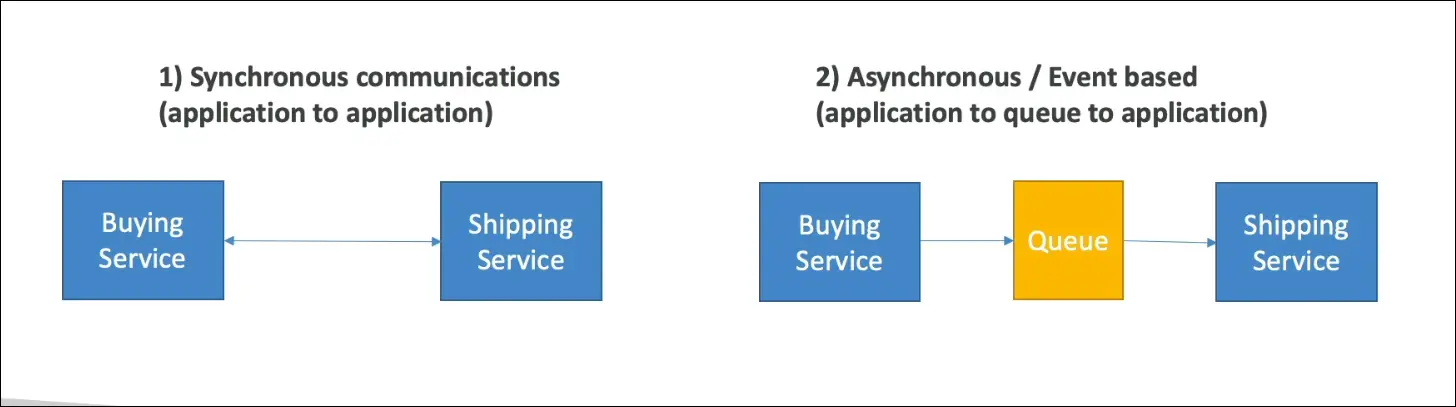
A. Synchronous Communication
- Definition: Applications directly communicate in real-time.
- Example:
A Buying Service directly calls a Shipping Service to start shipment after a purchase. - Characteristics:
- Real-time and direct connection.
- Immediate response required.
- If one service is down or overloaded, the other is affected.
- Disadvantages:
- Not resilient to failures or traffic spikes.
- Services are tightly coupled.
B. Asynchronous (Event-Based) Communication
- Definition: Applications communicate indirectly through an intermediate system (like a queue).
- Example:
The Buying Service places an order message in a queue, and the Shipping Service processes it later. - Characteristics:
- Services are decoupled (operate independently).
- Enables scalability and fault tolerance.
- Allows buffering during high traffic (prevents overload).
Benefits of Decoupling
- Prevents cascading failures.
- Handles sudden spikes in workload (e.g., encoding 1000 videos instead of 10).
- Each service can scale independently.
- Improves reliability and flexibility.
AWS Services for Cloud Integration
| Service | Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQS (Simple Queue Service) | Queue-based (asynchronous) | Stores messages until they are processed by consumers. | Task queues, decoupling producer/consumer. |
| SNS (Simple Notification Service) | Pub/Sub model | Sends messages to multiple subscribers (email, SQS, Lambda, etc.). | Event notifications, broadcasting updates. |
| Kinesis | Real-time streaming | Collects, processes, and analyzes real-time data streams. | Real-time analytics, log or metrics streaming. |
Key Takeaways
- Synchronous = Direct communication, simple but tightly coupled.
- Asynchronous = Indirect communication via queue, scalable and fault-tolerant.
- Use SQS, SNS, or Kinesis to build decoupled, resilient, and scalable AWS architectures.
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service)
- SQS (Simple Queue Service) is used to decouple applications.
- It is fully managed and serverless.
- One of the oldest AWS services (over 10 years old).
- Handles any scale — from 1 msg/sec to tens of thousands/sec.
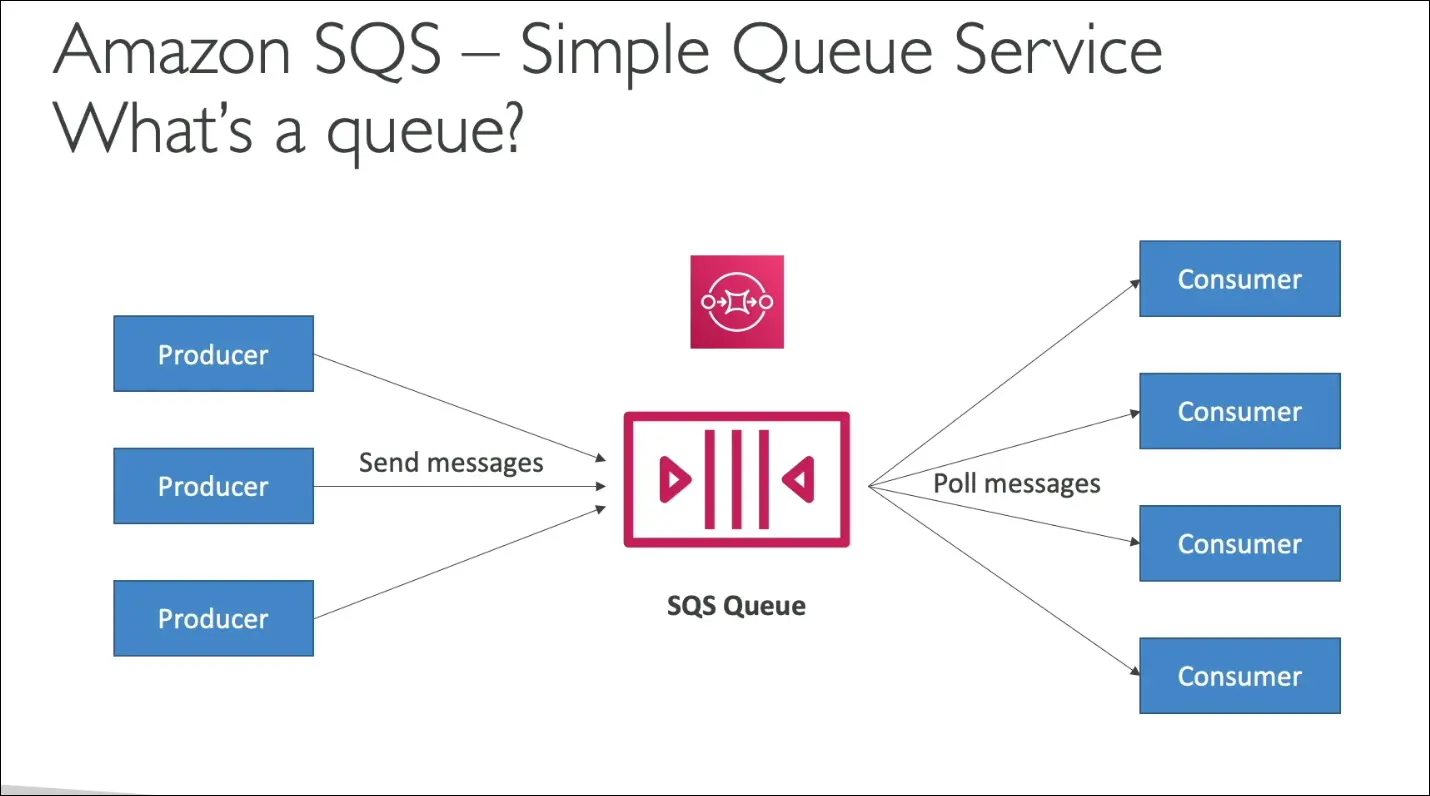
Concept of a Queue
- A queue stores messages between producers and consumers.
Flow:
- Producers send messages into the queue.
- Messages are stored temporarily.
- Consumers poll (retrieve) messages.
- Once processed, the message is deleted from the queue.
Producers and consumers are decoupled — they work independently and at different speeds.
Key Characteristics
- Default retention: 4 days
- Maximum retention: 14 days
- No limit on number of messages in a queue.
- Low latency: Less than 10 ms for publish/subscribe.
Exam Tip
If you see the keyword “decouple applications,” think of SQS.
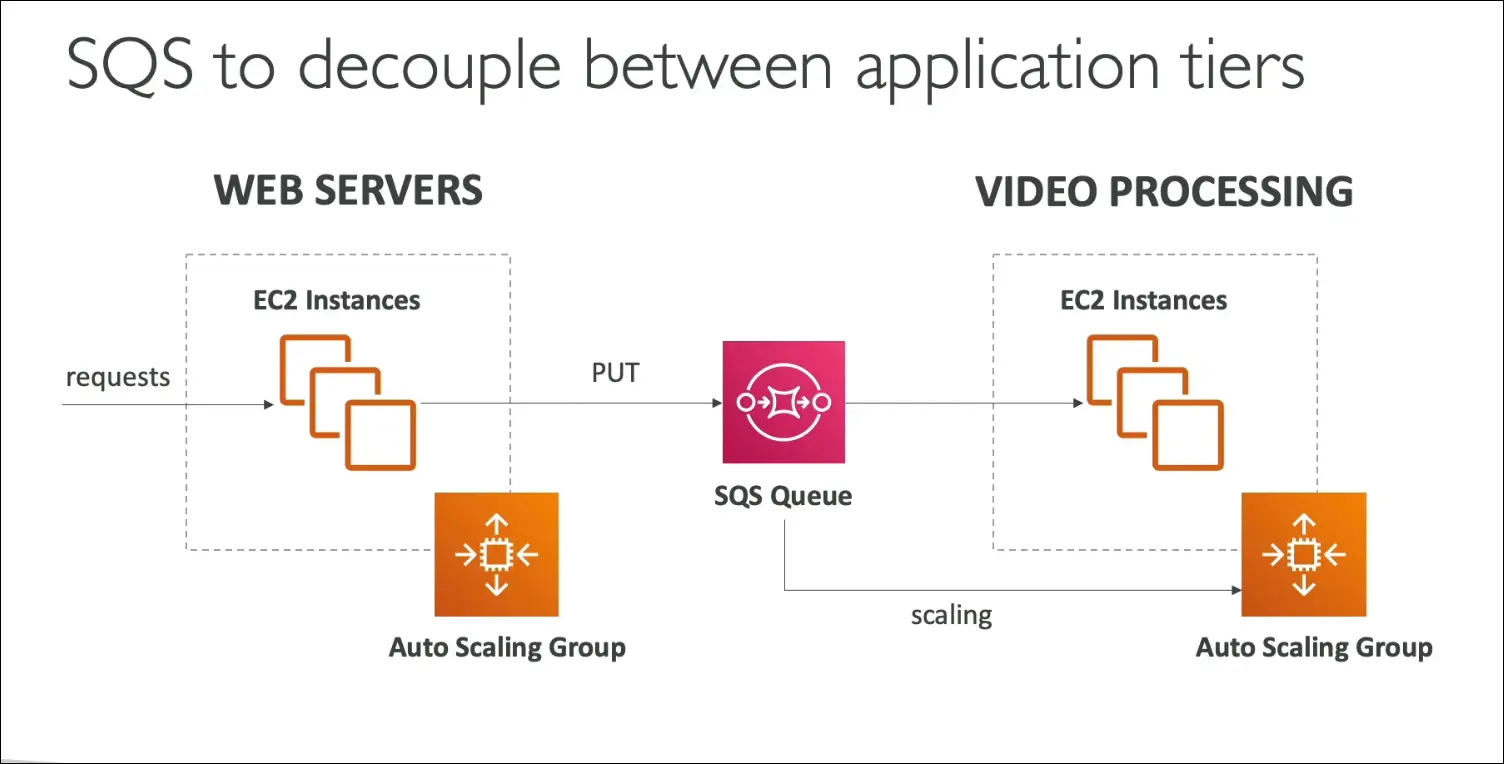
Example Architecture
- Scenario: A web application processes videos.
- Setup:
- Web tier: EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer.
- Instead of sending videos directly to the processing app,
the web servers send messages to an SQS queue. - A video processing layer (another EC2 Auto Scaling Group) polls messages from SQS and processes them.
Benefits:
- Both layers are fully decoupled.
- They scale independently based on load or number of messages.
- Efficient, fault-tolerant, and cost-effective.
FIFO Queues (First-In-First-Out)
- Guarantee that messages are processed in order (1, 2, 3, 4…).
- Use Case: When order of operations matters.
- Regular (Standard) queues may deliver messages out of order.
- Remember: FIFO = Ordered message delivery.

Summary Table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Message Queue (Asynchronous Communication) |
| Fully Managed | Yes |
| Retention | 4 days (default), 14 days (max) |
| Latency | <10 ms |
| Scaling | Automatic, unlimited throughput |
| Queue Types | Standard (unordered) and FIFO (ordered) |
| Use Case | Decouple application layers, handle spikes, improve reliability |
Core Benefit
SQS decouples application components to enable independent scaling and fault tolerance.
Amazon Kinesis Data Streams (KDS)
Definition and Purpose
- Amazon Kinesis is used for real-time big data streaming.
- Kinesis Data Streams (KDS) collects, processes, and analyzes real-time streaming data at any scale.
- Commonly appears in the exam when referring to real-time data processing or data streams.
Core Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Kinesis Data Streams (KDS) | Captures and processes streaming data in real time. |
| Kinesis Data Firehose | Delivers (loads) data streams to destinations such as S3, Redshift, or OpenSearch. |
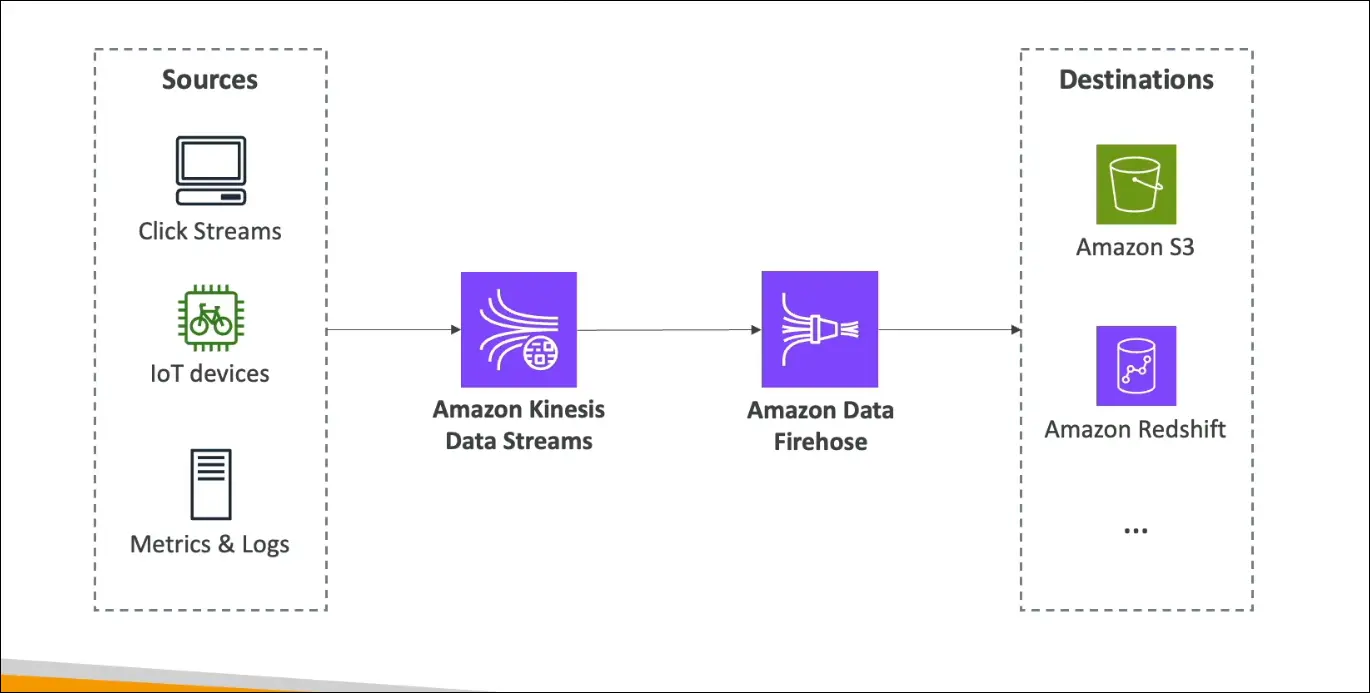
3. Example Workflow
- Data Sources (Fast Data):
- Website clicks
- IoT devices
- Application logs and metrics
- Kinesis Data Streams:
- Ingests and processes data in real time.
- Kinesis Data Firehose:
- Sends processed data to storage or analytics services like:
- Amazon S3 (for long-term storage)
- Amazon Redshift (for data warehousing)
- Amazon OpenSearch Service (for search and visualization)
- Sends processed data to storage or analytics services like:
Key Features
- Handles real-time, high-volume data.
- Scalable to any number of data producers and consumers.
- Integrates easily with other AWS services.
Exam Tips
- If the question mentions “real-time streaming”, “live analytics”, or “data ingestion at scale”, the answer is usually Amazon Kinesis.
- For delivering data from streams to destinations (like S3 or Redshift), the correct service is Kinesis Data Firehose.
Summary
| Concept | Key Point |
|---|---|
| Kinesis Data Streams | Collect and process real-time data |
| Kinesis Data Firehose | Deliver data to AWS destinations |
| Use Case Examples | Website clicks, IoT sensor data, app logs |
| Exam Focus | Know that Kinesis = real-time streaming data service |
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service)
Purpose
- Amazon SNS is used to send one message to many receivers.
- It helps decouple applications through a Publish/Subscribe (Pub/Sub) model.
- Main use case: fan-out notifications to multiple systems or users at once.
How It Works
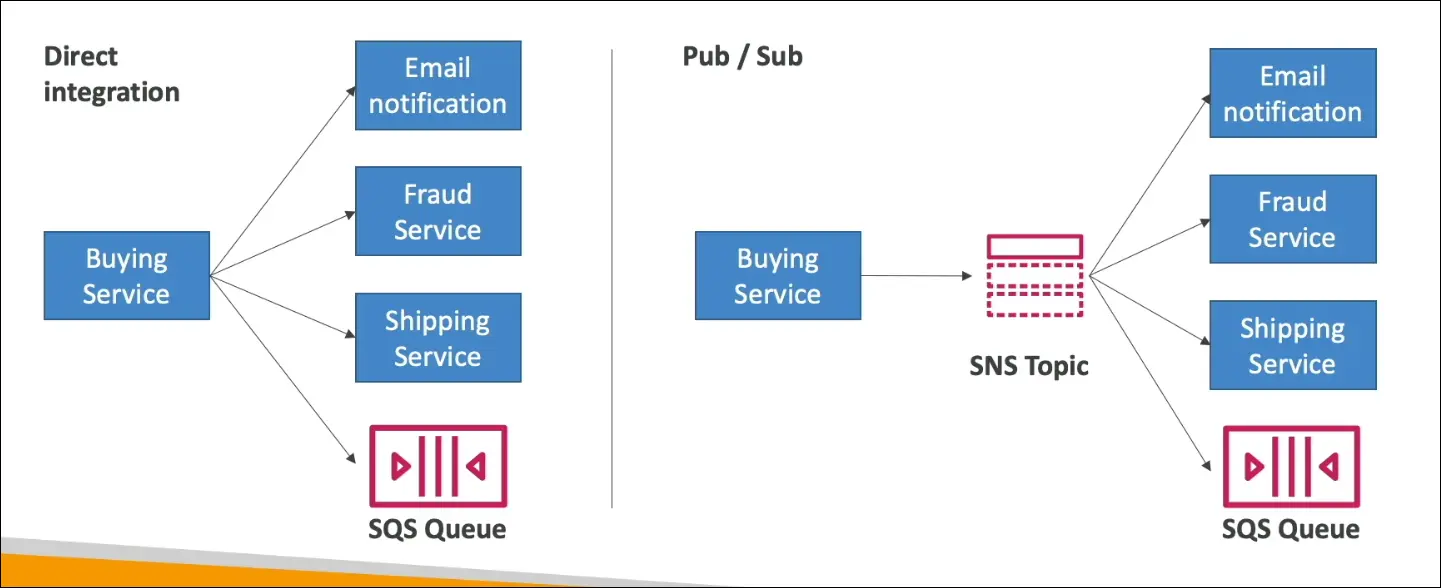
Without SNS:
- A single service (like a Buying Service) must send notifications individually to:
- Email service
- Fraud detection service
- Shipping service
- SQS Queue
- This requires multiple direct integrations (complex and inefficient).
With SNS (Pub/Sub Model):
- The Buying Service (Publisher) sends a single message to an SNS Topic.
- The SNS Topic automatically forwards that message to:
- Email notifications
- Fraud service
- Shipping service
- SQS Queues
- Each subscriber gets a full copy of every message.
Key Concepts
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Publisher | The sender of the message (e.g., Buying Service). |
| Topic | The SNS resource that receives and distributes messages. |
| Subscriber | The receivers (e.g., SQS queues, Lambda functions, emails). |
| Subscription | The connection between a topic and a subscriber. |
Important Details
- Each subscriber receives all messages sent to the topic.
- SNS vs SQS:
- SNS: All subscribers get all messages (fan-out model).
- SQS: Messages are shared among consumers (competing consumers model).
Limits
| Limit | Description |
|---|---|
| Max Subscriptions per Topic | 12 million |
| Max Topics per Account (Soft Limit) | 100,000 |
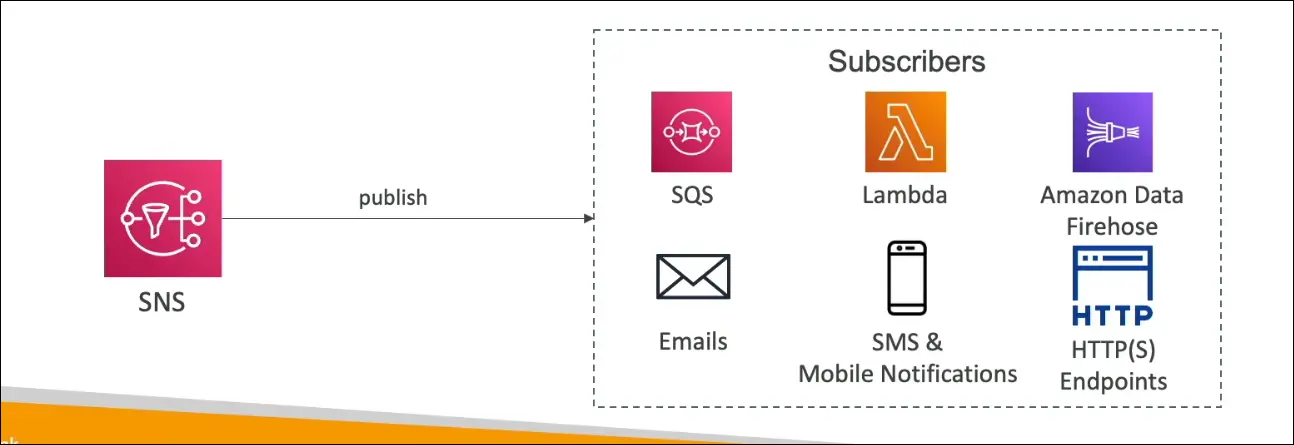
Supported Destinations
SNS can publish messages to:
- Amazon SQS (to queue messages)
- AWS Lambda (to trigger functions)
- Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose (to stream data)
- Email notifications
- SMS (text messages)
- Mobile push notifications
- HTTP/HTTPS endpoints
Exam Tips
| Keyword | Think of |
|---|---|
| Notification | Amazon SNS |
| Publish/Subscribe | Amazon SNS |
| Fan-out to multiple systems | Amazon SNS |
| Message delivery to multiple subscribers | Amazon SNS |
✅ If the question says “send one message to many subscribers,” the correct answer is SNS.
Summary
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Type | Pub/Sub messaging service |
| Publisher | Sends messages to SNS topic |
| Subscribers | Receive all messages from the topic |
| Integration Targets | SQS, Lambda, Firehose, Email, SMS, HTTP/S |
| Exam Keyword | “Notification” → Amazon SNS |
Amazon MQ
Purpose
- Amazon MQ is a managed message broker service for open-source messaging protocols.
- It is used when migrating existing on-premises applications to AWS without re-engineering them to use SQS/SNS APIs.
Why Use Amazon MQ
- SQS and SNS are AWS-native and use AWS-specific APIs.
- Many legacy applications use open protocols like:
- MQTT
- AMQP
- STOMP
- OpenWire
- WSS (WebSocket Secure)
- Rewriting these apps for SQS/SNS can be costly, so Amazon MQ provides compatibility with existing systems.
Supported Message Brokers
- RabbitMQ
- ActiveMQ
Both are popular open-source message brokers for enterprise messaging systems.
Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Managed Broker | AWS handles provisioning, maintenance, and patching. |
| Supports Open Protocols | Compatible with MQTT, AMQP, STOMP, OpenWire, etc. |
| Queue + Topic Support | Provides both queue (like SQS) and topic (like SNS) features in one service. |
| High Availability | Can be deployed in Multi-AZ setup with automatic failover. |
Scalability & Performance
- Does not scale automatically like SQS or SNS.
- Runs on dedicated servers (broker instances), so you might face server limitations.
- Ideal for enterprise workloads needing specific messaging protocols, not for massive cloud-native scaling.
When to Use
Use Amazon MQ only if:
- You are migrating to AWS and already use open protocols.
- You need RabbitMQ/ActiveMQ compatibility for existing applications.
Otherwise, use SQS or SNS for:
- Better scalability
- Serverless architecture
- Deep AWS integration
Comparison Summary
| Feature | SQS/SNS | Amazon MQ |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | AWS proprietary APIs | Open standard protocols (MQTT, AMQP, etc.) |
| Scaling | Fully managed, auto-scaled | Limited by broker instance size |
| Management | Serverless | Managed brokers (servers) |
| Best For | Cloud-native apps | Legacy apps migrating to AWS |
| Availability | Highly scalable | Multi-AZ for HA (manual setup) |
Exam Tip
✅ If the question mentions open protocols (MQTT, AMQP, STOMP, OpenWire) or RabbitMQ/ActiveMQ, the correct answer is Amazon MQ.
✅ If it mentions scalability, serverless, or native AWS messaging, the correct answer is SQS/SNS.
Summary
