Deployments & Managing Infrastructure at Scale
CloudFormation Overview
- What it is:
- AWS service for Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
- Declarative way of describing AWS resources (you state what you want, not how to create it).
- Supports almost all AWS resources.
- Example use case:
- Define: Security Group, 2 EC2 instances using that SG, an S3 bucket, a Load Balancer.
- CloudFormation will automatically create all resources in the correct order with the exact configuration.
Benefits of CloudFormation
- Infrastructure as Code
- No manual creation of resources.
- Changes reviewed via code review (improves control and governance).
- Cost Advantages
- Resources in a stack are automatically tagged for easier cost tracking.
- Can estimate costs before deployment.
- Enables cost-saving automation, e.g., delete stacks at 5 PM, recreate at 8 AM.
- Productivity
- Easily destroy and recreate infrastructure.
- Generates diagrams of resources and their relationships.
- Declarative programming: CloudFormation figures out dependencies (e.g., DynamoDB before EC2).
- Reusability
- Use existing templates from AWS docs or community.
- Almost everything in AWS is supported.
- If not, use Custom Resources.
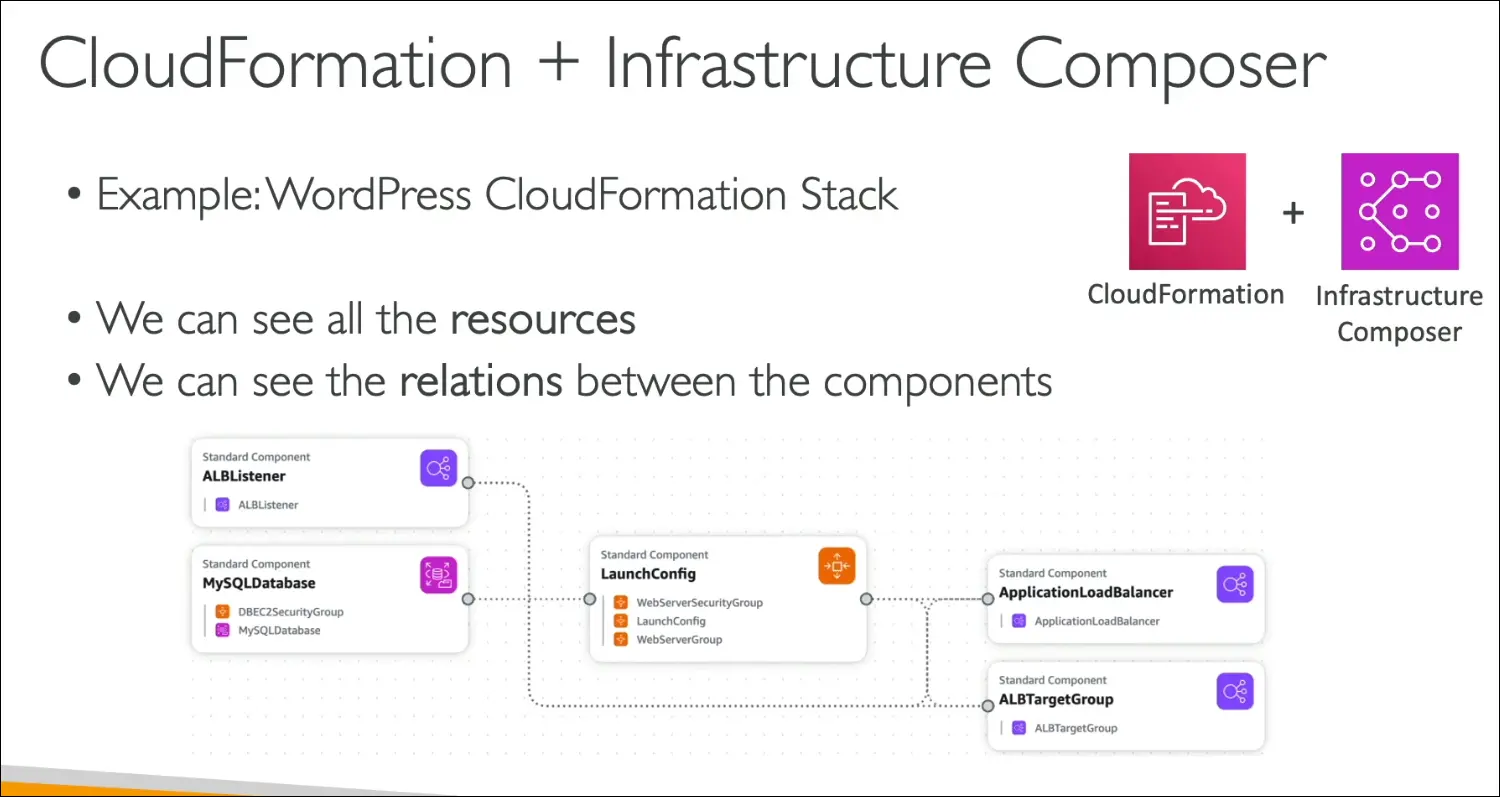
Visualization
- Infrastructure Composer can visualize stacks.
- Example: WordPress stack diagram shows ALB Listener, DB, Security Groups, Launch Config, etc.
- Helps understand relations between components.
Exam Tips (AWS CCP)
- CloudFormation = Infrastructure as Code.
- Used for:
- Repeating architectures across environments (dev, prod).
- Deploying to multiple regions or AWS accounts.
- Remember: Declarative, automated, cost-efficient.
Key takeaway: CloudFormation is the core AWS service for Infrastructure as Code, making deployments reproducible, scalable, and cost-efficient.
AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK)
What is CDK?
- AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK) is a tool to define cloud infrastructure using familiar programming languages.
- Alternative to writing raw CloudFormation templates (YAML/JSON).
- Supported languages: Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, Java, .NET.
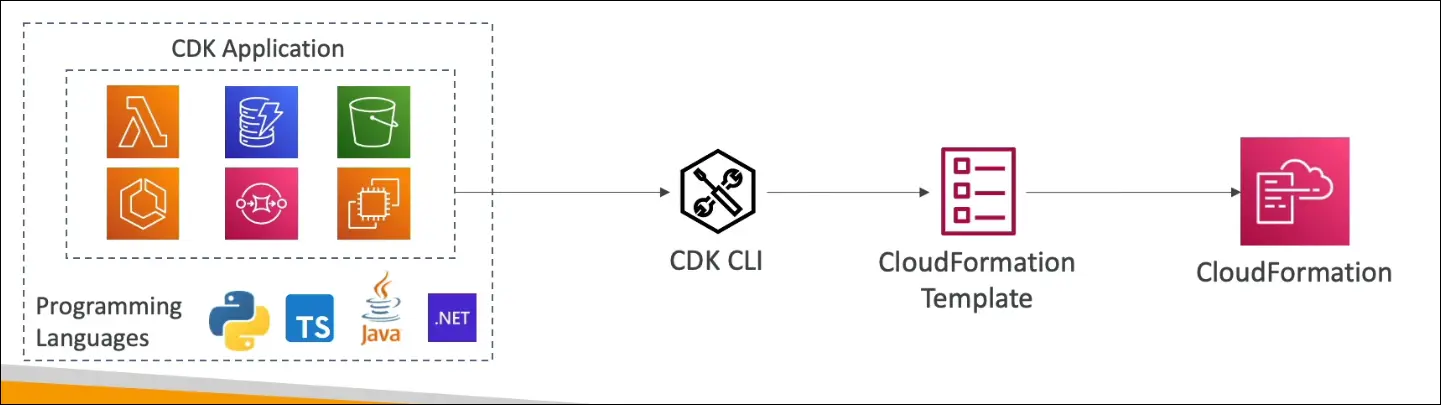
How It Works
- Write infrastructure code in your chosen language (e.g., Python, TypeScript).
- CDK compiles it into a CloudFormation template (JSON or YAML).
- The template is then deployed via CloudFormation to provision resources.
Benefits of CDK
- Infrastructure as Code but in a programming language you already know.
- Type safety and familiar constructs.
- Can use loops, conditionals, reusable functions.
- Easier and faster to develop compared to raw YAML/JSON.
- Can deploy infrastructure and runtime code together.
- Useful for Lambda functions, ECS/EKS containers, etc.
Example Use Case
- Write a CDK app in Python:
- Define a Lambda function, DynamoDB table, other services.
- CDK app → compiled into CloudFormation template → deployed.
- Example (TypeScript/JavaScript CDK snippet):
- Define a VPC.
- Define an ECS cluster.
- Define an Application Load Balancer (ALB) with a Fargate service.
- CDK compiles this into a CloudFormation template for deployment.
Exam Tips (AWS CCP)
- CDK is built on top of CloudFormation.
- Lets you use familiar languages instead of YAML/JSON.
- Still results in a CloudFormation template under the hood.
- Best for developers who want:
- Reusable code patterns.
- Type safety.
- To deploy infra + app code together.
Key takeaway: CDK = CloudFormation, but written in real programming languages, giving you more flexibility, reusability, and speed.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
Context and Motivation
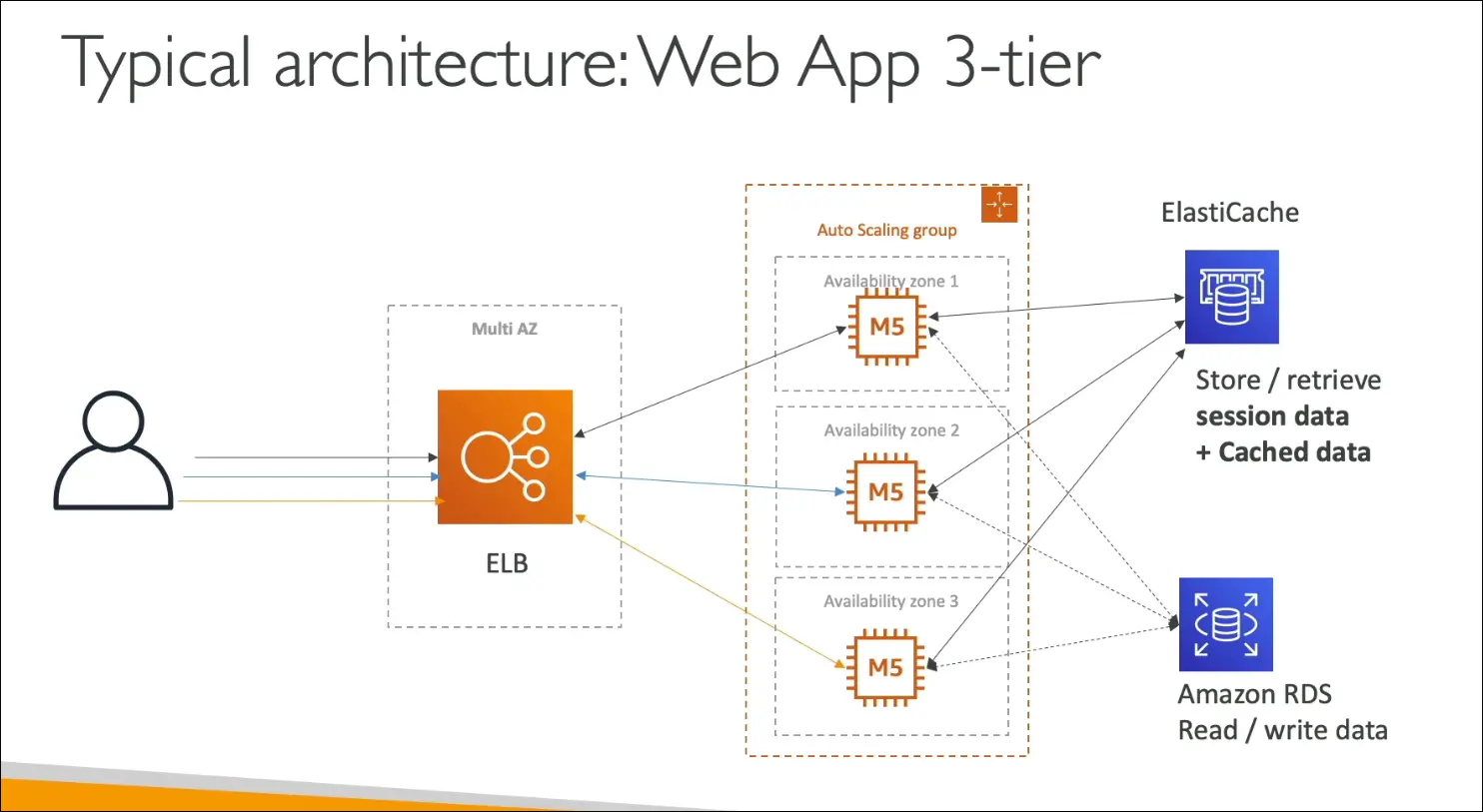
- Most web apps on AWS follow a 3-tier architecture:
- Load Balancer (multi-AZ for HA).
- EC2 instances in an Auto Scaling Group.
- Database (Amazon RDS).
- Optional cache (ElastiCache for sessions/cached data).
- This can be built manually or via CloudFormation.
- But developers usually don’t want to manage infrastructure, they just want to deploy code and let AWS handle scaling, load balancing, and provisioning.
What is Elastic Beanstalk?
- Elastic Beanstalk (EB) = Platform as a Service (PaaS) on AWS.
- Provides a developer-centric view for deploying apps.
- Under the hood it still uses:
- EC2, ASG, ELB, RDS, etc.
- You focus only on application code.
- AWS handles provisioning, scaling, monitoring, health checks, and deployment strategies.
Key Features
- Managed Service (free to use, pay for underlying resources).
- Handles:
- EC2 OS setup and configuration.
- Deployment strategy (configurable).
- Auto Scaling and Load Balancing.
- Health monitoring and metrics (via CloudWatch).
- Developer responsibility = only application code.
Beanstalk Architectures
- Single instance
- Best for development/test environments.
- Load balanced + Auto Scaling group
- Best for production web apps.
- Worker environments
- For non-web apps (background jobs, workers).
Supported Platforms
- Programming languages and runtimes:
- Go, Java, .NET, Node.js, PHP, Python, Ruby.
- Container support:
- Docker (single, multi, preconfigured images).
- Many application stacks are supported, making it flexible.
Health Monitoring
- Beanstalk includes a health agent on each EC2 instance.
- Pushes metrics to CloudWatch.
- Beanstalk console provides:
- Application health checks.
- Monitoring dashboards.
- Health event logs.
Cloud Service Models Recap
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) → EC2, RDS, etc.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service) → Beanstalk.
- SaaS (Software as a Service) → Services where you only use the software, no infra management (e.g., WorkMail, Chime).
Exam Tips
- Elastic Beanstalk = PaaS.
- Developer responsibility = only app code.
- AWS handles infra (provisioning, scaling, monitoring).
- Free to use, but pay for underlying resources.
- Three deployment models: Single Instance, LB + ASG, Worker.
- Provides built-in health monitoring.
AWS CodeDeploy
What is CodeDeploy?
- A service to automatically deploy applications.
- More flexible and independent compared to Elastic Beanstalk or CloudFormation.
- You can deploy to:
- EC2 instances
- On-Premises servers
Why CodeDeploy?
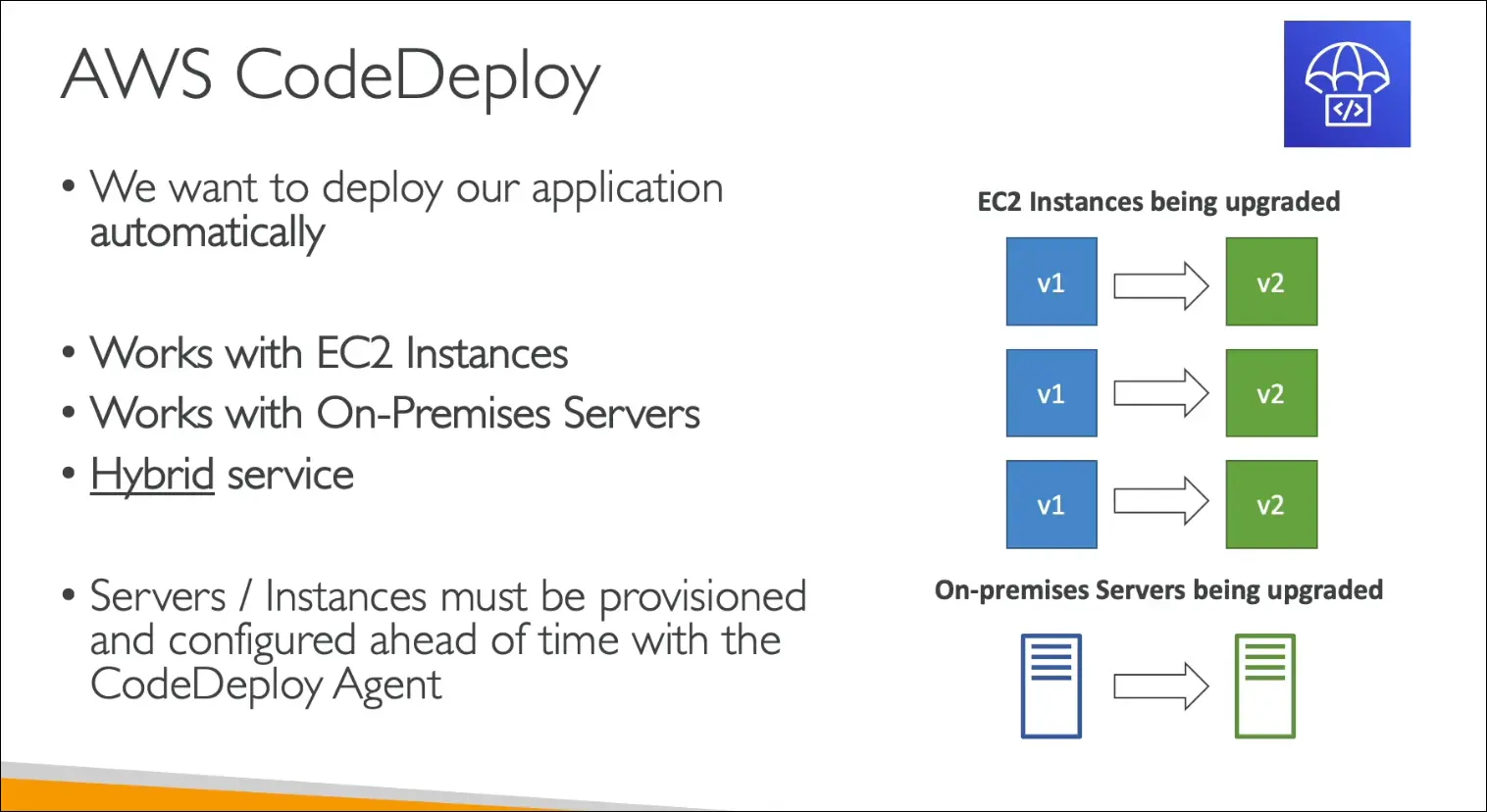
- Helps upgrade applications (e.g., v1 → v2) seamlessly.
- Works in hybrid environments:
- AWS Cloud (EC2).
- On-premises data centers.
- Useful for organizations migrating to AWS, since it keeps a consistent deployment method.
Key Features
- Hybrid deployment service (EC2 + On-Premises).
- Supports any type of server, but:
- You must provision servers yourself.
- You must install the CodeDeploy Agent on those servers.
- Provides a single interface to manage deployments across environments.
Deployment Flow
- Prepare your servers (EC2 or On-Premises).
- Install the CodeDeploy Agent.
- Define your application deployment (AppSpec file).
- CodeDeploy handles automatic upgrade from one version to another.
Benefits
- Simplifies application updates across many servers.
- Ensures consistency in deployment process between cloud and on-premises.
- Helps in cloud migration by standardizing deployments.
Exam Tips
- CodeDeploy = automated app deployment service.
- Works with both EC2 and On-Premises servers (hybrid).
- Requires CodeDeploy Agent installed on target servers.
- You are responsible for server provisioning and configuration.
- Great for migrations and hybrid deployments.
AWS CodeCommit
What is CodeCommit?
- Fully-managed source control service by AWS.
- Based on Git (G-I-T).
- Similar to GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket, but hosted within AWS.
Purpose
- Store your application code securely in AWS.
- Acts as a version control repository.
- Used before pushing/deploying application code to servers.
Benefits
- Versioning: Tracks code changes automatically, with rollback capability.
- Collaboration: Makes it easy for developers to work together on projects.
- Fully managed: No need to manage infrastructure.
- Scalable and highly available: Runs on AWS infrastructure.
- Secure: Resides inside your AWS account, not a public platform.
- AWS integration: Works seamlessly with CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, CodePipeline, etc.
Exam Tips
- CodeCommit = Git-based repo service in AWS.
- Alternative to GitHub or other Git hosting platforms.
- Key value: private, secure, scalable, AWS-integrated source control.
- Great for organizations that want full control of their code inside AWS.
AWS CodeBuild
What is CodeBuild?
- Fully managed build service on AWS.
- Purpose: compile source code, run tests, and produce deployment-ready packages.
- Output = artifacts that can be deployed (e.g., by CodeDeploy).
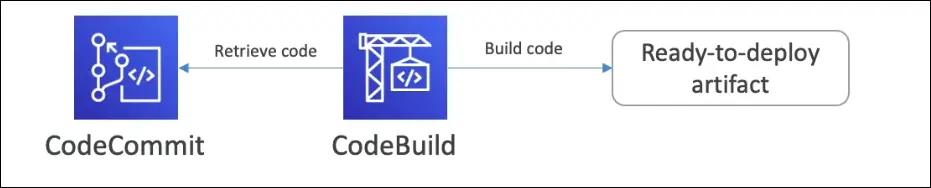
How it Works
- Developer pushes code → stored in CodeCommit (or another repo).
- CodeBuild retrieves code.
- Runs build scripts (defined by you, usually in
buildspec.yml). - Compiles, tests, packages.
- Produces artifacts ready for deployment.
Features
- Fully managed & serverless: no servers to manage.
- Continuously scalable: handles multiple builds concurrently.
- Highly available & secure: built on AWS infra.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing: only pay for build time.
- Automatic build triggers: runs every time code is updated in CodeCommit (or other source).
Benefits
- Automates the build and test process in CI/CD pipelines.
- Integrates tightly with CodeCommit, CodePipeline, and CodeDeploy.
- Lets developers focus on coding, while AWS handles build infrastructure.
Exam Tips
- CodeBuild = build service (compile, test, package).
- Works with CodeCommit (source) and CodeDeploy (deployment).
- Serverless, scalable, pay-as-you-go.
- Key output = artifacts ready for deployment.
AWS CodePipeline
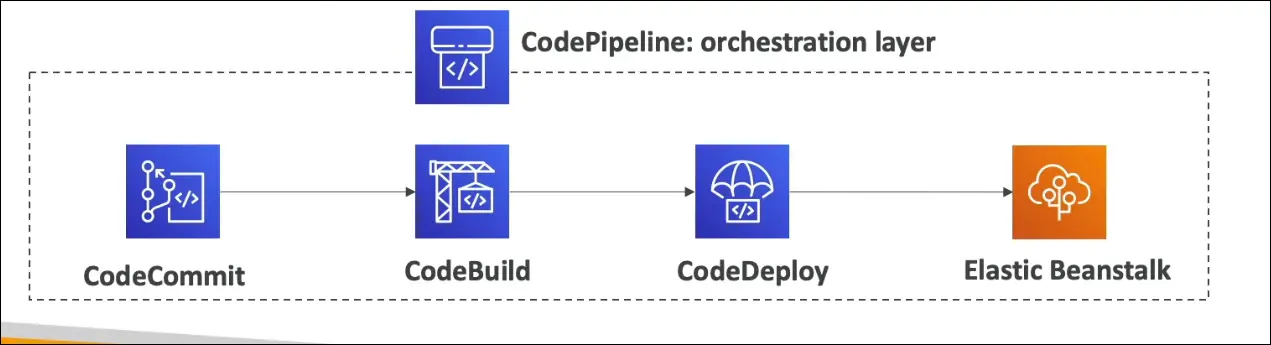
What is CodePipeline?
- A fully managed orchestration service for automating the flow of code changes.
- Connects CodeCommit, CodeBuild, and CodeDeploy into a pipeline.
- Ensures that code is automatically built, tested, and deployed to production.
Use Case Example
- Developer pushes code to CodeCommit.
- CodeBuild compiles code and runs tests.
- CodeDeploy (or Elastic Beanstalk) deploys the application to servers.
- Orchestration is handled by CodePipeline.
Key Features
- CICD (Continuous Integration & Continuous Delivery):
- Every code push triggers build, test, and deploy.
- Fully Managed: No servers to manage.
- Integrations: Works with AWS services and third-party tools.
- AWS: CodeCommit, CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, Elastic Beanstalk, CloudFormation.
- External: GitHub, custom plugins, third-party services.
- Benefits:
- Fast delivery, rapid updates.
- Central to AWS CICD ecosystem.
Exam Tip
- Anytime you see orchestration of pipelines in AWS exam questions, think AWS CodePipeline.
AWS CodeArtifact
What is CodeArtifact?
- A fully managed artifact management service by AWS.
- Stores and retrieves software packages (dependencies).
- Secure, scalable, and cost-effective alternative to running your own artifact system.
Why Do We Need It?
- Software projects often rely on code dependencies (e.g., libraries, frameworks).
- Traditionally:
- Set up custom artifact management on Amazon S3 or EC2.
- This adds complexity and maintenance overhead.
- CodeArtifact removes that burden by providing a ready-to-use solution.
Key Features
- Integrates with common dependency managers:
- Java: Maven, Gradle
- JavaScript: npm, Yarn
- Python: pip, twine
- .NET: NuGet
- Central secure repository for teams.
- Works seamlessly with CodeCommit and CodeBuild:
- CodeBuild can fetch dependencies directly from CodeArtifact.
Benefits
- Fully managed by AWS (no servers to manage).
- Secure by default.
- Scales with your project.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing.
Exam Tip
- If a question mentions artifact management system or storing dependencies → answer is AWS CodeArtifact.
AWS Developer Tools Comparison
| Service | Purpose / Function | Managed? | Typical Workflow Role | Integrations | Exam Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CodeCommit | Secure, private Git-based repository for source code. | Fully managed | Store and manage source code | Integrates with CodeBuild, CodePipeline, CodeDeploy, IDEs (e.g., VS Code) | Think source control |
| CodeBuild | Build service: compiles source, runs tests, produces deployable artifacts. | Fully managed, serverless | Build & Test | Works with CodeCommit, CodePipeline, CodeArtifact | Think build and test automation |
| CodeDeploy | Deployment service: deploys applications to EC2, Lambda, on-premises. | Fully managed | Deploy | Integrates with EC2, Lambda, ECS, CodePipeline | Think deployment automation |
| CodePipeline | Orchestration service for CICD pipelines (connects CodeCommit → CodeBuild → CodeDeploy). | Fully managed | Orchestrator (CI/CD pipeline) | Works with all AWS Developer Tools, GitHub, Jenkins, custom plugins | Think pipeline orchestration |
| CodeArtifact | Artifact management system for storing/retrieving software packages (dependencies). | Fully managed | Store & retrieve dependencies | Integrates with npm, pip, Maven, Gradle, NuGet, CodeBuild | Think dependency management |
AWS Systems Manager (SSM)
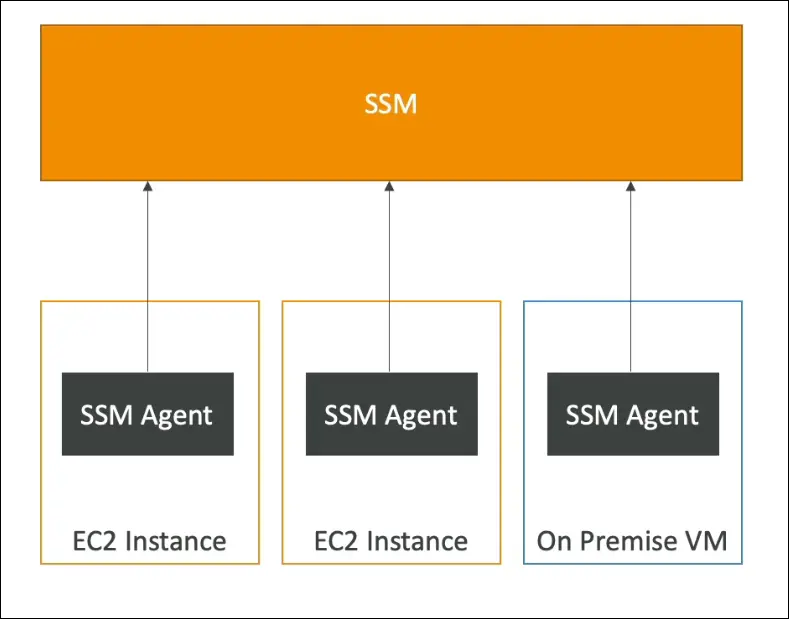
- AWS Systems Manager (SSM) helps manage EC2 instances and on-premises servers at scale.
- A hybrid AWS service (works for both AWS and on-prem).
- Provides operational insights and a suite of 10+ tools.
Key Features
- Hybrid support: Works for AWS and on-premises servers/VMs.
- Automation: Run commands across the fleet.
- Patch Management: Automated patching for compliance.
- Configuration Management:
- Store configurations with SSM Parameter Store.
- Apply consistent configurations across servers.
- Cross-platform support: Linux, Windows, macOS, Raspberry Pi.
How It Works
- SSM Agent must be installed on instances/servers.
- Runs in the background, communicates with SSM.
- Preinstalled on Amazon Linux AMI and some Ubuntu AMIs.
- The agent reports back to the SSM service in AWS.
- Once installed:
- Run commands across all servers.
- Patch the fleet.
- Apply consistent configurations.
Exam Tips
- Keywords: fleet management, patching, hybrid environment, run command.
- If asked how to patch or run commands across EC2 + on-prem servers → Answer: SSM.
- If an instance isn’t managed by SSM → likely an agent issue.
Benefits
- Simplifies management at scale.
- Hybrid ready.
- Improves compliance and security.
- Centralized operations for multiple environments.
AWS Systems Manager – Parameter Store
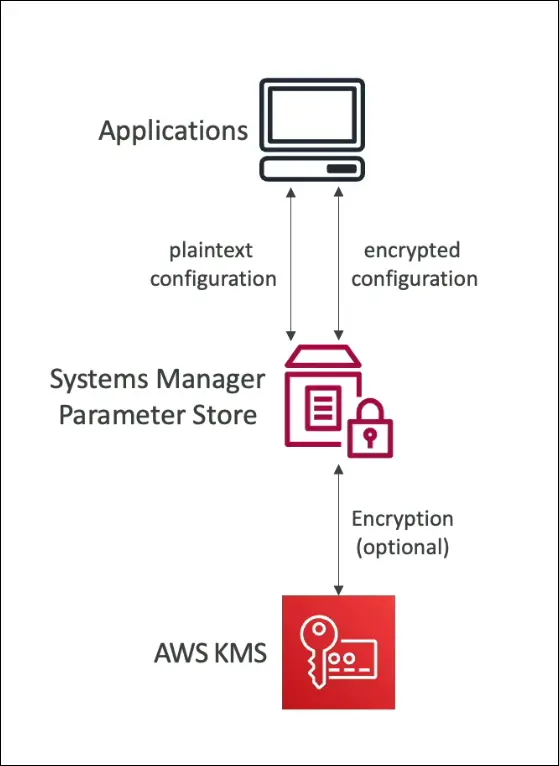
Purpose
- Central place to store configuration and secrets securely.
- Examples: API keys, passwords, application configs.
- Serverless, scalable, durable, secure.
Key Features
- Storage Options
- String: plain text value.
- StringList: list of values.
- SecureString: encrypted using AWS KMS (for sensitive data like passwords).
- Security
- Access controlled by IAM policies (who can read/write specific parameters).
- Optional encryption with KMS for secure parameters.
- Versioning
- Every time you edit a parameter, a new version is created.
- Useful for tracking and rollback.
- Integration
- Applications, EC2, and Lambda functions can retrieve parameters directly.
- Reduces need to hardcode secrets in code or environment variables.
- Tiers
- Standard (free): basic usage.
- Advanced (paid): higher throughput, larger sizes, more features.
Hands-On Example (from transcript)
- Create parameter named demo parameter.
- Choose type: String, StringList, or SecureString.
- Store value like
"my configuration parameter". - Retrieve it anytime via console, CLI, or SDK.
- Parameter versions are maintained automatically.
- Can delete parameters anytime.
Benefits
- Centralized configuration management.
- Secure storage of sensitive values (encrypted with KMS).
- Easier auditing and tracking with version history.
- Simplifies deployments by removing secrets from code.
Exam Tip: Use Parameter Store when you need a secure, serverless, versioned, and IAM-controlled place to store configuration and secrets.
AWS Deployment and Developer Services
Deployment Services
- CloudFormation
- AWS-only tool for Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
- Works with almost all AWS resources.
- Uses templates to deploy infra in multiple Regions and accounts.
- Enables repeatable and automated deployments.
- Elastic Beanstalk
- PaaS (Platform as a Service).
- Limited to supported languages and Docker.
- Deploy apps consistently with known architecture, e.g. Load Balancer + EC2 + RDS.
- AWS manages scaling and environment details.
- CodeDeploy
- Deploys and updates apps onto servers (EC2 or on-premises).
- Hybrid service (works AWS + on-prem).
- Automates deployments at scale.
- Systems Manager
- Hybrid service (AWS + on-premises).
- Manage servers at scale (patch, configure, run commands).
- Useful for fleet management.
Developer Services
- CodeCommit
- Private Git-based repo in AWS.
- Secure, version-controlled code storage.
- CodeBuild
- Serverless build service.
- Compiles, tests, and packages code.
- CodeDeploy
- Repeated here because it bridges deployment + developer services.
- Deploys app code to servers.
- CodePipeline
- Orchestration tool for CI/CD.
- Automates flow: Source → Build → Test → Deploy → Provisioning.
- CodeArtifact
- Secure, managed storage for software packages & dependencies.
- Supports multiple ecosystems (npm, Maven, pip, etc).
- AWS CDK (Cloud Development Kit)
- Define infra using real programming languages (TS, JS, Python, Java, etc).
- Compiles into CloudFormation templates for deployment.
Exam Tips:
- CloudFormation vs CDK: CDK uses code, CloudFormation uses YAML/JSON.
- Elastic Beanstalk: Quick PaaS deployment with limited flexibility.
- CodeDeploy: Hybrid deployment (on-prem + AWS).
- CodePipeline: End-to-end automation of CI/CD.
- CodeArtifact: Think npm registry but inside AWS.
- Systems Manager: Manage fleet of servers, both AWS + on-prem.