Docker Introduction (Before ECS)
What is Docker?
- Docker = software development platform to deploy applications.
- Traditional way: install apps directly on Linux → works but not portable.
- Docker way: package app into containers.
Docker Containers
- Run the same way everywhere (no compatibility issues).
- Works with any programming language, OS, technology.
- Easier to maintain, deploy, and scale.
- Scaling containers = seconds.
- Powerful and widely used for modern app deployment.
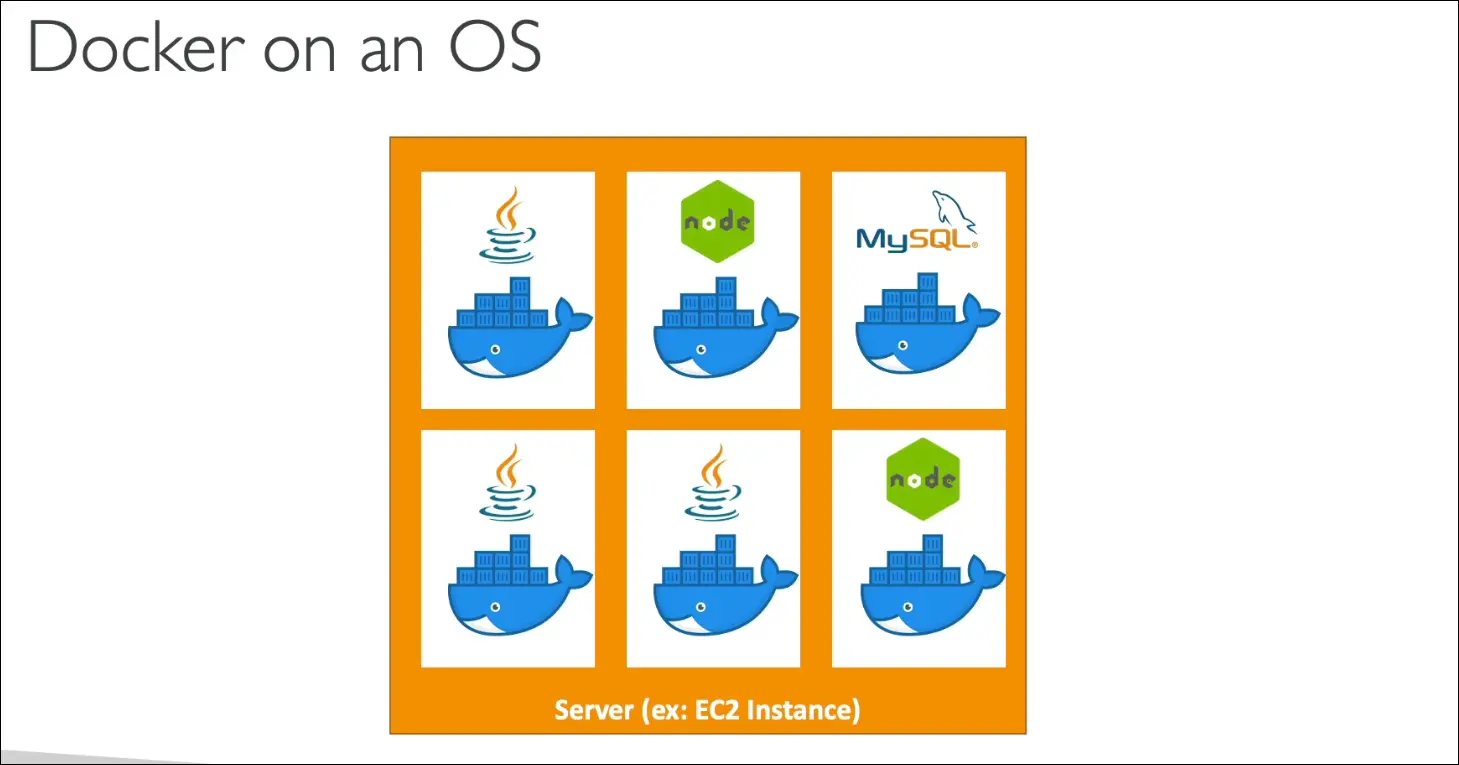
Docker on EC2
- You can run multiple containers on the same EC2 instance:
- Example: Java, Node.js, MySQL all on one EC2.
- Docker Images = blueprint for containers.
- Stored in Docker Repositories.
Docker Repositories
- Public: Docker Hub (base images for OS, DBs, languages).
- Private: Amazon ECR (Elastic Container Registry) for private images.
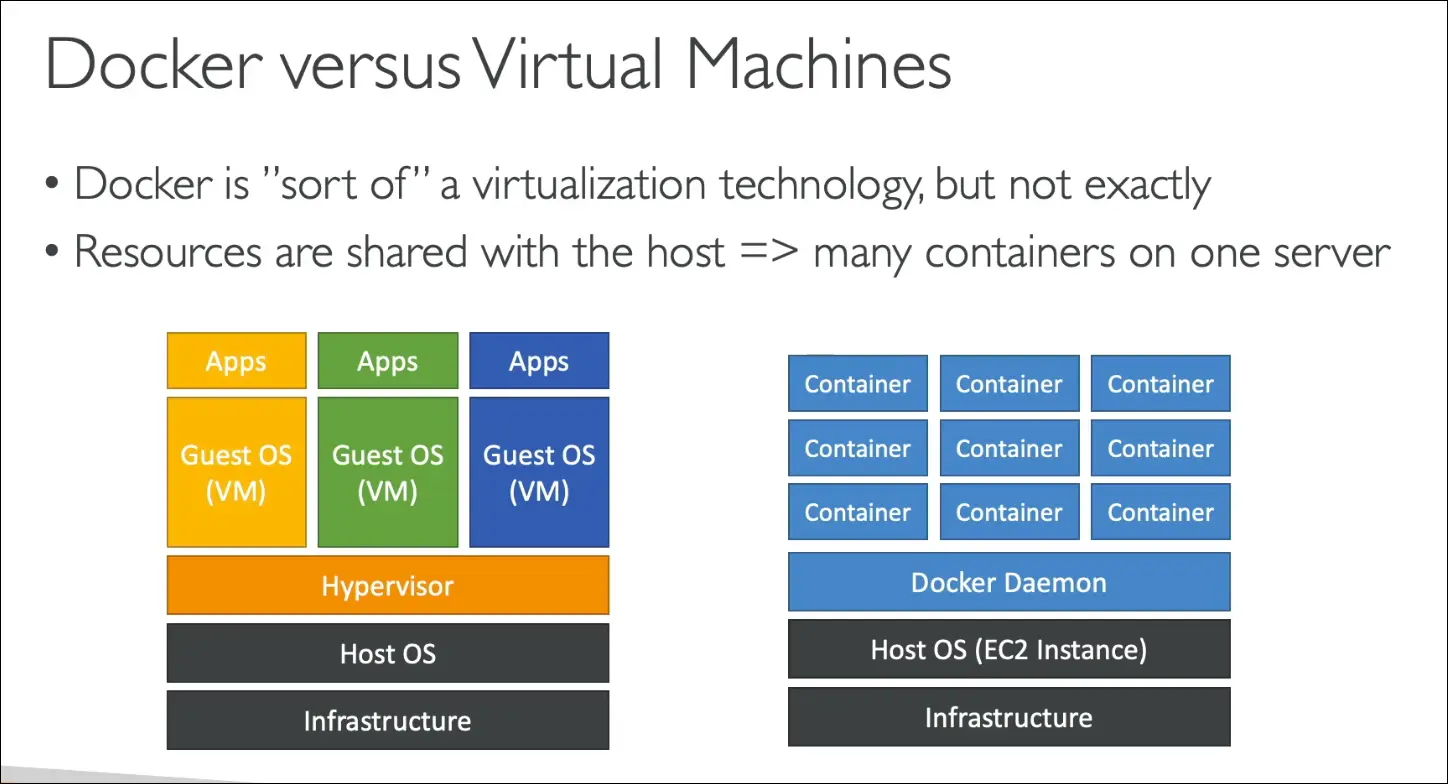
Docker vs Virtual Machines
- Docker ≠ full virtualization.
- VM approach:
- Infrastructure → Host OS → Hypervisor → Guest OS → Apps.
- Each VM has its own OS → heavier.
- Docker approach:
- Infrastructure → Host OS (EC2) → Docker Daemon → Containers.
- Containers share resources with host.
- Lightweight, faster, easier to scale.
Exam Tip
- You don’t need deep Docker knowledge for CCP.
- Just know:
- Docker = containerization.
- Images stored in repos (Docker Hub, ECR).
- Lighter than VMs.
- ECS = AWS service to run/manage Docker containers.
ECS, Fargate, and ECR (AWS CCP)
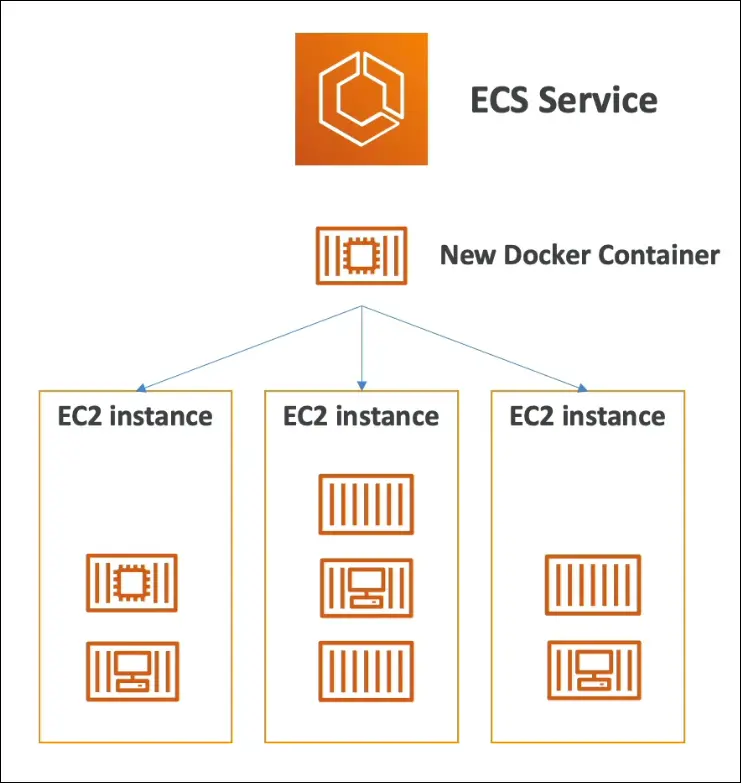
ECS (Elastic Container Service)
- Used to launch Docker containers on AWS.
- Requires provisioning & managing EC2 instances yourself.
- AWS manages container lifecycle (start/stop).
- Can integrate with Application Load Balancer.
- ECS decides which EC2 instance will host each container.
- Exam Tip: “Run Docker containers on AWS → think ECS.”
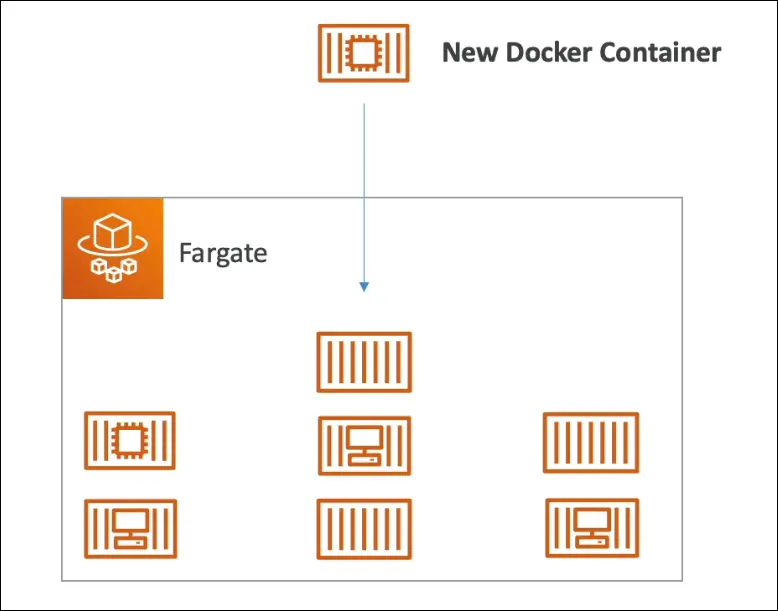
Fargate
- Also runs Docker containers on AWS.
- No need to manage EC2 instances (serverless).
- You only define CPU and RAM per container.
- AWS runs containers automatically (location abstracted).
- Simpler than ECS, preferred for ease of use.
- Exam Tip: Fargate = serverless container solution.
ECR (Elastic Container Registry)
- Private AWS Docker image registry.
- Stores Docker images for ECS and Fargate.
- Alternative to public repos (like Docker Hub).
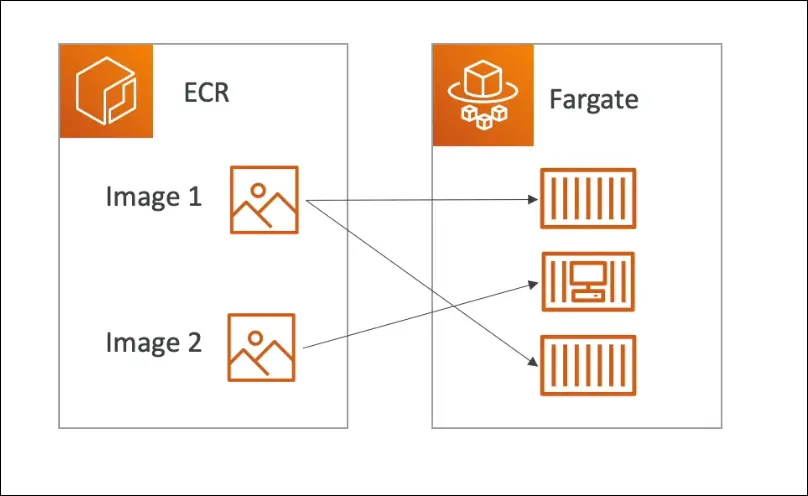
Comparison
- ECS → Run containers, manage EC2 infra yourself.
- Fargate → Run containers, AWS manages infra (serverless).
- ECR → Store Docker images for ECS/Fargate.
Exam Key Point: Know the difference between ECS, Fargate, and ECR.
Amazon EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service)
What is EKS?
- Elastic Kubernetes Service (managed service for Kubernetes on AWS).
- Allows you to launch & manage Kubernetes clusters.
Kubernetes Recap
- Open-source system for:
- Managing
- Deploying
- Scaling containerized apps.
- Typically uses Docker containers, but supports other container runtimes too.
- Runs workloads in Pods (smallest deployable units).
Where Pods Run in EKS
- On EC2 instances → You manage infra.
- On AWS Fargate → Fully serverless, AWS manages infra.
Why EKS?
- Running Kubernetes yourself = complex.
- EKS provides a managed Kubernetes control plane.
- Great for multi-cloud or hybrid setups → Kubernetes is cloud agnostic.
- Works on AWS, Azure, GCP, or on-premises.
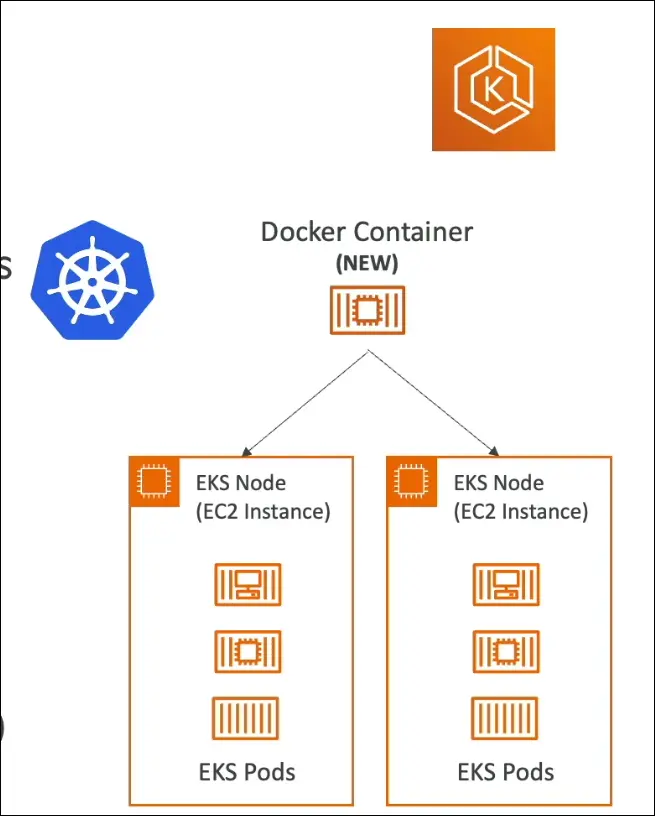
Exam Tip
- If you see “Kubernetes on AWS” → Think Amazon EKS.
- If you see “multi-cloud containers” → Think Kubernetes (EKS on AWS).
Quick Recall:
- ECS → AWS-native container orchestration.
- EKS → Kubernetes (open-source, cloud-agnostic) managed by AWS.
- Fargate → Serverless option for both ECS & EKS.
- ECR → Stores container images for ECS/EKS/Fargate.
Serverless (Intro)
What is Serverless?
- A paradigm where developers don’t manage servers.
- Developers focus on deploying code / functions only.
- Originally started as Function as a Service (FaaS) with AWS Lambda.
- Today, “serverless” = fully managed services (compute, storage, DB, messaging).
Key Points
- Serverless ≠ no servers → servers exist, but you don’t provision, manage, or see them.
- AWS handles scaling, provisioning, availability.
Examples of Serverless Services
- Amazon S3 → Storage (infinite scale, no servers managed).
- Amazon DynamoDB → Serverless database, auto scales with load.
- AWS Fargate → Run containers without managing EC2 instances.
- AWS Lambda → Pioneer of serverless, runs functions in the cloud.
Exam Tip
- If a question says “no server management” or “serverless compute” → Think Lambda.
- If it’s serverless database → DynamoDB.
- If it’s serverless storage → S3.
- If it’s serverless containers → Fargate.
Quick Recall: Serverless = No server management, fully managed, auto-scaling, pay-per-use.
What is AWS Lambda?
- Serverless compute service where you run functions instead of servers.
- Functions are short-lived and event-driven (triggered when needed).
- No need to provision or manage servers.
Comparison with EC2
- EC2: Always running, billed for uptime, scaling with Auto Scaling Groups (slower and more complex).
- Lambda: Runs only on demand, billed per request and execution time, scaling is automatic.
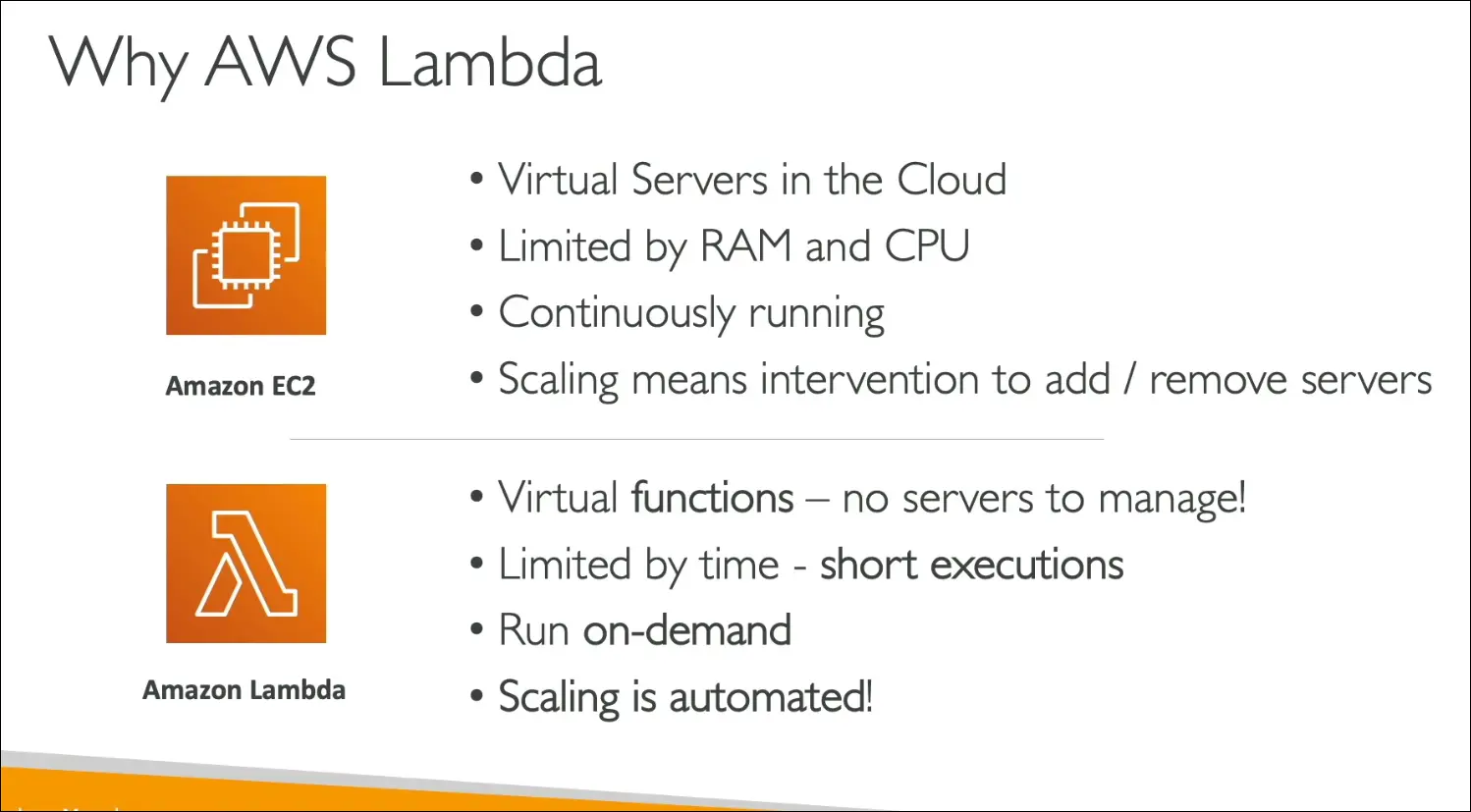
Benefits of AWS Lambda
- Pricing:
- Free tier: 1M requests/month and 400,000 GB-seconds/month.
- After free tier: $0.20 per 1M requests.
- Pay only per request and compute time.
- Scalability: Automatically scales with demand.
- Integration: Works with many AWS services (S3, DynamoDB, CloudWatch, etc).
- Monitoring: Built-in with CloudWatch.
- Resource allocation: Up to 10 GB RAM per function. Increasing RAM also boosts CPU and network.
Supported Languages
- Native: Node.js, Python, Java, C# (.NET Core, PowerShell), Ruby.
- Custom runtimes: Rust, Go, etc via Custom Runtime API.
- Can run container images, but for Docker workloads prefer ECS or Fargate in exams.
Common Use Cases
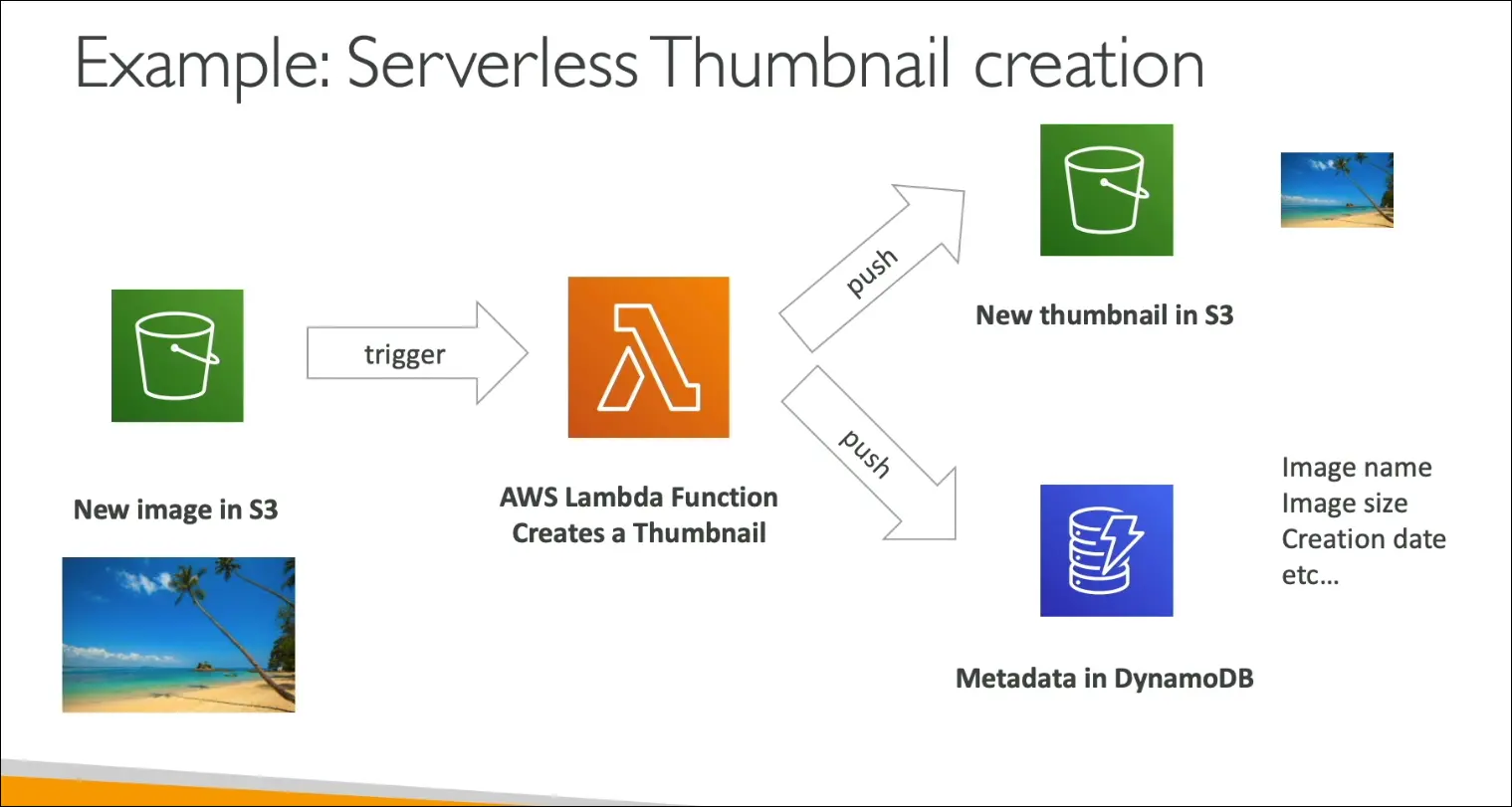
- Serverless thumbnail creation:
- User uploads image to S3 → triggers Lambda → generates thumbnail → saves to S3 → metadata to DynamoDB.
- Fully serverless and event-driven.
- Serverless CRON jobs:
- Instead of EC2 CRON, use CloudWatch Events / EventBridge to trigger Lambda on schedule.
- Example: Run a script every hour.
Key Exam Points
- Lambda = event-driven, reactive, serverless.
- Pay attention to S3 + Lambda use cases.
- For containers, prefer ECS/Fargate over Lambda in exam context.
- Main languages to remember: Node.js and Python.
Amazon API Gateway
What is API Gateway?
- Fully managed, serverless service to create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs in AWS.
- Used to expose Lambda functions (or other backends) as REST or WebSocket APIs.
- Provides the entry point for clients to interact with serverless apps.
Typical Serverless Use Case
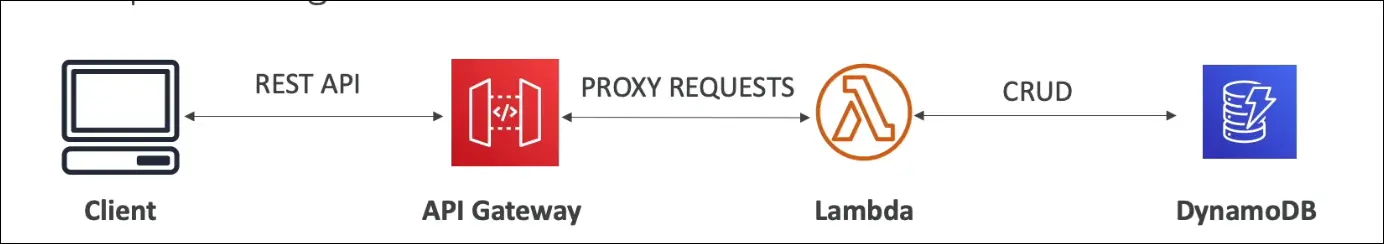
- Lambda + DynamoDB (serverless compute + serverless database).
- Problem: Lambda is not directly exposed to external clients.
- Solution: API Gateway acts as a front door, exposing a REST API or WebSocket API.
- Flow:
- Client → API Gateway → Lambda → DynamoDB.
Key Features
- Scalable and serverless (no infrastructure to manage).
- Supports:
- RESTful APIs.
- WebSocket APIs (real-time communication).
- Security and Access Control:
- User authentication (e.g., Cognito, IAM).
- API keys.
- Throttling (limit requests).
- Monitoring via CloudWatch.
Exam Tips
- If the question mentions serverless API → Answer is API Gateway + Lambda.
- If it’s about real-time streaming API → Think API Gateway WebSockets.
- Remember: It is serverless, fully managed, and auto-scales.
Quick Recall:
API Gateway = Serverless API front door for Lambda and other AWS services.
AWS Batch
What is AWS Batch?
- Fully managed batch processing service.
- Runs hundreds of thousands of batch jobs at any scale.
- A batch job = has a start and an end (not continuous like streaming jobs).
How It Works
- You submit or schedule jobs into a batch queue.
- AWS Batch dynamically provisions compute (EC2 or Spot Instances).
- Automatically allocates right amount of vCPU, memory, and storage.
- Runs jobs as Docker images on ECS (anything that runs on ECS can run on Batch).
Example Workflow
- User uploads images to Amazon S3.
- Upload triggers a Batch Job.
- Batch launches ECS cluster (EC2 or Spot Instances).
- Jobs run inside Docker containers.
- Processed output (e.g., filtered image) stored back in Amazon S3.
Features
- Scales automatically (adds/removes instances as needed).
- Cost optimization (Spot Instances supported).
- No need to manage infrastructure, focus only on jobs.
- Supports any runtime if packaged as a Docker container.
AWS Batch vs AWS Lambda
| Feature | AWS Lambda | AWS Batch |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Limit | 15 minutes max | No time limit (depends on EC2) |
| Runtime | Limited languages | Any runtime (via Docker image) |
| Storage | Small temp storage | EC2 storage (EBS, Instance Store) |
| Infra Type | Serverless | Managed service (uses EC2/Spot) |
| Scaling | Fully serverless | Scales EC2 automatically |

Exam Tips
- If the workload = short, event-driven tasks → Use Lambda.
- If the workload = long-running, heavy compute, or custom runtime → Use AWS Batch.
- Remember: AWS Batch is not serverless, but AWS manages the EC2 infra for you.
Quick Recall:
AWS Batch = Managed batch job processing using ECS + EC2/Spot, scalable, no time limit, Docker-based.
Amazon Lightsail
Overview
- Stand-alone AWS service, simpler than core AWS services.
- Provides virtual servers, storage, databases, networking in one place.
- Offers low and predictable pricing.
Purpose
- Intended for people with little or no cloud experience.
- Hides complexities like networking, storage, and load balancing.
- Not for those learning AWS in depth (e.g., for certifications).
Features
- Simple to use compared to EC2, RDS, ELB, EBS, Route53.
- Provides preconfigured templates:
- Web apps: LAMP, Nginx, MEAN, Node.js.
- CMS / Websites: WordPress, Magento, Plesk, Joomla.
- Monitoring and notifications for resources.
Use Cases
- Deploy simple web apps or websites quickly.
- Great for development and test environments.
- Suitable when you want quick setup without AWS expertise.
Limitations
- Has high availability, but no auto-scaling.
- Limited AWS integrations.
- Rarely the right answer for professional AWS architecture.
Exam Tip
- If a question mentions:
- Beginner with no cloud experience
- Needs quick start with predictable cost
- Doesn’t want to configure networking, scaling, or storage
→ The answer is Lightsail.
- Otherwise, Lightsail is usually the wrong choice.
Summary
Docker on AWS
- Container technology to package and run apps.
- Run Docker on AWS via:
- ECS (EC2 launch type): run containers on your EC2 instances (you provision/manage infra).
- Fargate launch type: run containers serverlessly (no infra to manage).
AWS Fargate
- Serverless compute engine for containers (works with ECS and EKS).
- No need to manage EC2 instances.
- Transparent scaling, only pay for resources used.
Amazon ECR
- Elastic Container Registry.
- Stores and manages private Docker images.
- Integrated with ECS and Fargate.
AWS Batch
- Managed batch processing service.
- Runs batch jobs across a fleet of EC2 instances.
- Built on top of ECS.
- Great for long-running, scheduled, or parallel jobs.
Amazon Lightsail
- Simple cloud platform with predictable, low pricing.
- Provides servers, storage, and databases.
- Great for beginners with little cloud experience.
- Exam note: often a distractor, rarely correct answer.
⚡ AWS Lambda
- Serverless Function-as-a-Service (FaaS).
- Seamless scaling: from 1 to thousands of requests/sec.
- Pricing = execution time + memory allocated + number of requests.
- Supports many languages.
- Can run Docker containers, but only if they implement the Lambda Runtime API.
- For arbitrary Docker images → use ECS or Fargate, not Lambda.
- Invocation limit: max 15 minutes.
- Use cases:
- Process files (e.g., image resizing on S3 upload).
- Serverless cron jobs.
API Gateway + Lambda
- API Gateway = serverless service to expose Lambda functions as APIs.
- Provides:
- HTTP endpoint
- Authentication & security
- API keys, throttling, monitoring
Quick Recap Table
| Service | Type | Key Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| ECS (EC2) | Containers | Run containers on self-managed EC2 |
| ECS (Fargate) | Containers | Serverless containers, no infra management |
| ECR | Containers | Store private Docker images |
| Batch | Batch Jobs | Long-running, scheduled jobs (built on ECS) |
| Lightsail | Simple Cloud | Beginners, simple apps, predictable pricing |
| Lambda | Serverless | Short-running functions (≤ 15 min) |
| API Gateway | API Mgmt | Expose Lambda as HTTP APIs |